PAC
Employment in trade grows for third consecutive year, and reaches 10.5 million people
August 07, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: August 12, 2025 11h41 AM
Highlights
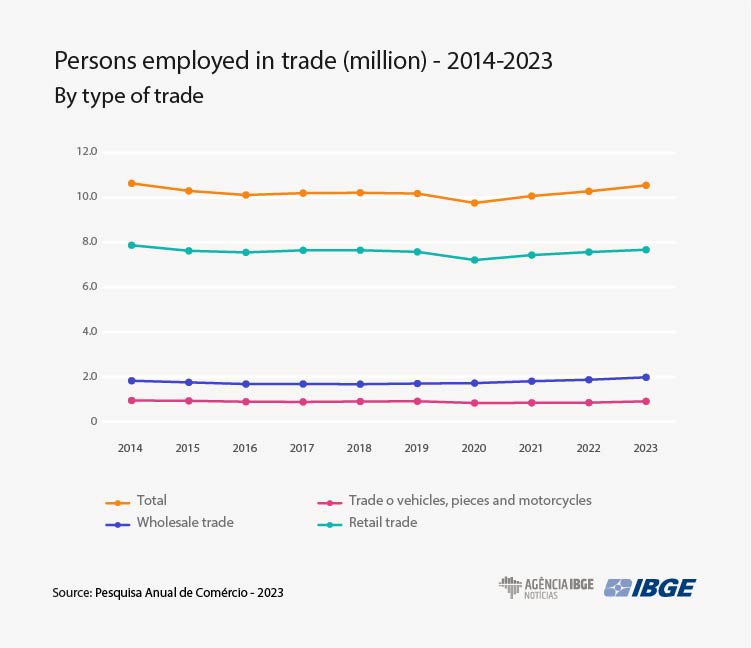
- Brazil had 10.5 million persons employed in formal trade in 2023, an increase of 2.6% (267,800) from 2022. This is the second-highest figure since 2007. Against the pre-pandemic period, in 2019, there was a 3.5% increase, adding 360,300 persons.
- The retail sector accounted for the biggest proportion of retail jobs, with 7.7 million workers, equivalent to 72.7% of the total. Wholesale trade employed two million persons, the highest number since 2007, representing 18.7%.
- The trade workforce in 2023 (10.5 million) received R$352.7 billion in wages, withdrawals, and other compensation
- In 2023, there were 1.5 million commercial companies in Brazil, distributed across 1.7 million local units. The net operating revenue of these companies totaled R$7.1 trillion.
- Wholesale trade (49.7%) accounted for the largest share of the sector's net operating revenue in 2023, followed by retail trade (41.2%) and sale of vehicles, parts, and motorcycles (9.1%).
- Trade of motor vehicles saw the largest decline in total net operating revenue, falling 2.2 percentage points (p.p.) between 2014 and 2023.
- São Paulo (29.2%) led the decline in the Southeast's share of the trade sector between 2014 and 2023, but both continued to have the highest revenue among states and Major Regions, respectively.
- The number of companies that traded online almost doubled between 2019 and 2023, rising from 1,900 to 3,700.

In 2023, there were 1.5 million commercial companies in Brazil, employing 10.5 million persons and encompassing 1.7 million local branches. Against 2022, employment increased by 2.6% (267,800 persons), marking the third consecutive year of growth. Compared to 2014, however, there was a 0.8% decrease (88,000 fewer persons), and compared to 2019, prior to the pandemic, there was a 3.5% increase (360,300). In 2023, the workforce received R$352.7 billion in salaries, withdrawals, and other compensation. Net operating revenue generated by commercial companies totaled R$7.1 trillion. This data is from the Annual Survey of Trade (PAC), released today (7) by the IBGE.
Since 2007, PAC has provided a detailed overview of the structural characteristics of the business segment of trade activity in Brazil, investigating the following topics: characterization of the revenue of commercial companies, structure of the trade margin, market concentration, employment profile of the trade sector, and structure of commercial companies in the Major Regions and their respective Federation Units.
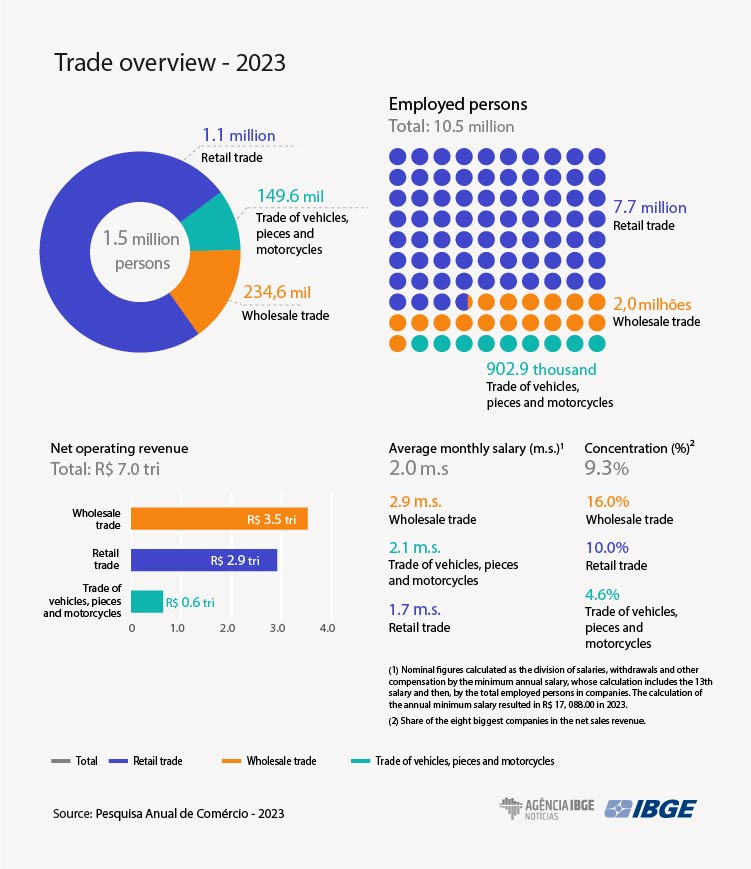
The retail sector accounted for the biggest proportion of jobs in trade, with 7.7 million workers, equivalent to 72.7% of the total. Among the retail activities with employment increase between 2014 and 2023, hypermarkets and supermarkets stood out, having the highest proportion of employed persons (15.1%), and a 30.6% increase in the number of workers (372,300 persons). Another highlight in the retail sector is the sale of pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic supplies, with a 21.3% increase, corresponding to 162,200 additional jobs over this 10-year period.
According to Marcelo Miranda, IBGE's structural analysis manager at the IBGE, the business profile explains the increase in employment in hypermarkets and supermarkets. "Hypermarkets and supermarkets require a large workforce to meet their various operational needs, such as product scalability, logistics and distribution, and customer service as well.
In addition to the sharpest increases, the retail sector recorded the sharpest drops in employment between 2014 and 2023. Sales of fabric, wearing apparel, footwear, and haberdashery fell by 332,900 persons (-24.6%), while IT, communications, and household articles lost 136,500 workers (-13.1%), and food products, beverage, and tobacco lost 118,900 persons (-9.4%).
Wholesale trade employed two million persons, the highest figure since 2007, and accounts for 18.7% of the total. Over the past 10 years, the activity with the highest employment growth was food products, beverage, and tobacco, which employed 39,300 more persons (9.2%), contributing to the record employment in the wholesale sector, according to Miranda.
Vehicles, pieces and motorcycle sales sector employed 902.9 thousand workers in 2023, equivalent to 8.6% of the total number of employed persons.
Retailers paid an average of two minimum wages, repeating the highest level in the time series
Retail companies paid an average of two minimum wages (m.w.) in 2023, repeating the 2022 result, the highest since 2007. The wholesale sector led with the highest average wage (2.9 m.w.), followed by trade of motorcycle, parts and vehicles (2.1 m.w.) and retail trade (1.7 m.w.). Against 2014, only vehicles, pieces and motorcycles saw a decline (-0.3 m.w.), while the other two sectors kept their average values.
Although retail employs more persons, wholesale paid the highest average wages were paid in wholesale. In this sector, the highlight was sale of fuels and lubricants (4.6 m.w.), which saw the biggest drop in the last 10 years (-1.7 m.w.); machinery, appliances and equipment, including IT and communication (4.3 minimum wages); and pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics and medical, optical and orthopedic articles, office supplies, stationery and household articles (4.0 minimum wages), whose average wages increased the most in the period (+0.4 minimum wages). The lowest wages were earned by representatives and agents in the wholesale sector (1.2 minimum wages), retail trade of food products, beverages and tobacco (1.3 minimum wages) and retail trade of textiles, wearing apparel, footwear and haberdashery (1.6 minimum wages). (1,6 s.m.).
The national average salary was 2.0 minimum wages in 2023, the Southeast region earned a higher salary (2.1 minimum wages), while the South region earned 2.0 minimum wages (2.0 minimum wages) at the same rate as the national average. The Central-West (1.9 minimum wages), North (1.7 minimum wages), and Northeast (1.5 minimum wages) paid below-average salaries. Over the past 10 years, commercial companies in the South and Central-West Regions increased their average salary by 0.1 minimum wage, while in the North Region, the average salary decreased by 0.1 minimum wage.
Led by wholesale trade, net revenue of trade sector was R$ 7.1 trillion in 2023
Commercial companies in Brazil recorded gross revenue of R$7.7 trillion in 2023. R$685.6 billion of that amount came from sales of vehicles, pieces, and motorcycles, R$3.8 trillion from wholesale trade, and R$3.2 trillion from retail trade. With the deduction of sales taxes, canceled sales, unconditional discounts, rebates, and other contributions, the sector's net operating revenue was R$7.1 trillion. It is worth highlighting that the monetary values mentioned in the survey correspond to current prices in 2023.
Wholesale trade (49.7%) contributed the most to net revenue generation, followed by retail trade (41.2%) and sales of vehicles, pieces, and motorcycles (9.1%). From 2014 to 2023, retail trade experienced the sharpest decrease in share, of 3.4 percentage points (p.p.). On the other hand, the sector's positive result in 2023 ended a five-year sequence of drops in share. Trade of vehicles, pieces, and motorcycle lost 2.6 percentage points, while wholesale trade grew by 5.9 percentage points in 10 years.
Three of the 22 segments in the trade sector generated most of the net operating revenue in 2023: wholesale trade of fuels and lubricants (11.8%), which grew 1.3 percentage points over the past 10 years and was the most representative activity in the year; hypermarkets and supermarkets (11.6%), which ranked first in the share ranking in 2014 and the second in 2023; and wholesale trade of food products, beverages, and tobacco (8.5%), which was the fourth most relevant activity in 2014 and the third in 2023.
The group that grew the most in terms of revenue share between 2014 and 2023 was wholesale trade of agricultural raw materials and live animals (3.2 percentage points), which advanced nine positions in the share ranking, having risen from the 15th to 6th position. Conversely, trade of motor vehicles (-2.2 percentage points) lost the biggest market share in 10 years, having dropped from the third to seventh position. Compared to the pre-pandemic period, hypermarkets and supermarkets stood out as the segment with the largest loss in net operating revenue (-1.3 percentage points).
Trade margin and trade concentration rates have decreased in 10 years
Trade margin, which represents the difference between net sales revenue (the largest portion of net operating revenue from the sale of goods) and the cost of goods sold, totaled R$1.6 trillion in 2023. Most of this amount came from retail (52.4%), followed by wholesale (40.0%) and vehicles, pieces, and motorcycles trade (7.6%).
Over the past 10 years, the trade margin rate, which measures a given sector's ability to increase sales revenue above acquisition costs and inventory changes, has fallen from 30.6% to 29.0%. In the same period, margins in retail (from 39.4% to 39.1%) and wholesale (from 25.1% to 22.5%) declined. Trade of vehicles, pieces, and motorcycles followed the opposite trend, rising from 20.3% to 23.4% in sales margins.
Of the 22 activity groups that comprise the trade sector, the highest sales margins were found in retail trade. Retail trade of cultural, recreational, and sporting goods grew 23.6 percentage points, the biggest increase since 2014 among all activities, with a margin rate of 84.9% in 2023. Next came retail trade of textiles, wearing apparel, footwear, and haberdashery (83.0%), which saw a 1.7 percentage point increase. Third in this ranking was retail trade of pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic products (62.8%), which expanded its margin rate by 4.6 percentage points.
In contrast, the three lowest trade margin rates were for the following activities: wholesale trade of fuels and lubricants, with a rate of 6.5% (a loss of 1.4 percentage points between 2014 and 2023); wholesale trade of agricultural raw materials and live animals, with a rate of 11.9% (a loss of 3.0 percentage points); and trade of motor vehicles, with 14.3% (an increase of 2.1 percentage points). The biggest margin rate loss was experienced by wholesale trade of pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic products, office articles, stationery, and household goods, which fell from 57.6% to 50.4% in 10 years.
As for trade concentration, measured by the R8 indicator (the higher the R8, the greater the concentration in the sector, segment, or group of activities), the survey showed a decrease in value. The eight largest companies in the tradesector increased their share from 10.2% in 2014 to 9.3% in 2023.
In retail, the R8 was 10.0% in 2023, a 1.3 percentage point increase over the past 10 years. Although the sector generally presents low concentration, the retail trade of computers, communications, and household goods stood out among the three largest companies, with a 41.2% share.
Wholesale trade (16.0%), on the other hand, saw a 4.6 percentage point drop in its R8 in 2023, from 2014. Two of the three highest-value activities in the indicator, among the 22 analyzed, were in the wholesale segment: wholesale trade of fuels and lubricants, with the highest R8 (56.6%); and wholesale trade of general merchandise, with an R8 of 34.0%. It is worth noting, however, that wholesale trade of fuels and lubricants saw a 17.7 percentage point drop, the biggest decrease compared to 2014.
Southeast Region participation in retail drops in 10 years, but remains highest in gross revenue
The Southeast Region accounted for 48.9% of gross resale revenue in 2023, but this share decreased from 2014, when it held 51.6%. This drop in share was primarily absorbed by the South, which fell from 19.7% to 20.9%, and the Central-West, which grew from 9.7% to 11.4% over the past 10 years.
The retail sector in the Southeast employed a total of 5.2 million persons in 2013, a 4.1% decrease against 2014, representing 223,400 fewer employed persons. The Northeast Region had 1.9 million employed workers, but also faced a decline in employment, with the departure of 5,000 professionals. The Central-West region ended 2023 with 947,500 professionals in trade; the Major Region had the highest absolute growth, of 6.5%, or 57,500 employed persons. The North Region had 378,900 workers in trade, after a 13.4% increase, or 44,900 employees, between 2014 and 2023. The South Region gained 38,000 persons (an increase of 1.8%) in the same period, reaching 2.1 million employed persons in formal trade.
Wholesale trade was predominant in 13 states, including the three in the South Region, while in the other 10, retail trade had increased weight in 2023. Over the last 10 years, Amazonas has become the most important retail trade location in terms of revenue, while Minas Gerais, Rio Grande do Sul, and Mato Grosso do Sul have seen the opposite trend.

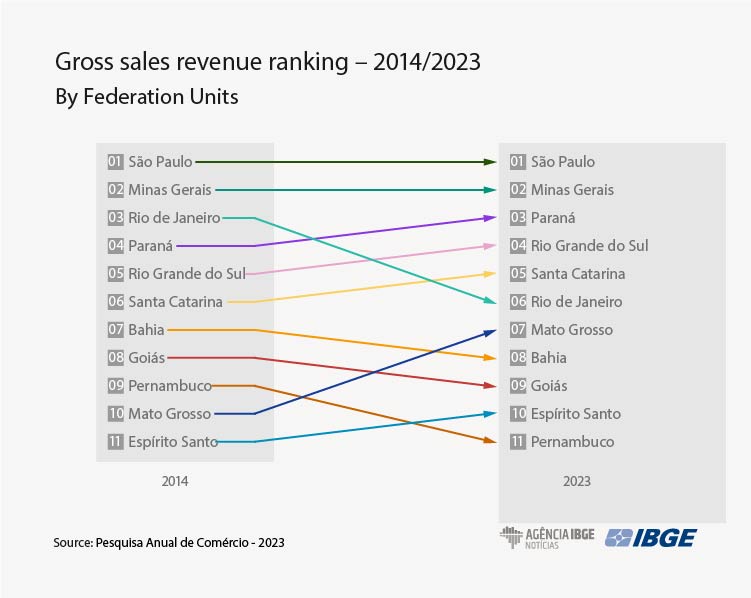
São Paulo was still the most representative state in the trade sector in financial terms, accounting for 29.2% of the country's gross revenue. However, over the last 10 years, it has lost ground, with a 2.2 percentage point decrease between 2014 and 2023, the biggest reduction among the states. Minas Gerais remained the second most important, with 10.0% of the total.
Rio de Janeiro, which in 2014 was the third best represented state, saw a 2.1 percentage point drop and, in 2023, fell to sixth place, with a 6.2% share. It was the state that lost the most positions regarding gross revenue between 2014 and 2023. Paraná (8.1%), Rio Grande do Sul (6.5%), and Santa Catarina (6.4%), which make up the South Region, surpassed Rio de Janeiro in this ranking. Mato Grosso was the state that gained the biggest share, rising from 2.9% in 2014 to 4.3% in 2023, and moving from tenth to seventh position.
Number of companies selling online nearly doubled in four years
The number of companies selling online grew 97.6% between 2019 and 2023, rising from 1,900 to 3,700 companies. PAC's online sales data only includes companies with 20 or more employees or with a high level of revenue, depending on the activity.
In the retail sector, the proportion of companies selling online went from 4.7% in 2019 to 8.6% in 2023. The retail activities selling online with the highest participation in 2023 were computer, communications, and household articles (19.7%), construction material (17.6%), textiles, wearing apparel, footwear, and haberdashery (15.9%), and pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic articles (13.8%).
The share of gross revenue from retail sold online rose from 5.3% in 2019 to 8.8% in 2023. However, there was a drop from 2022, when the share was 9.1%.
The activities with the bigges increases in gross revenue generated online between 2019 and 2023 were the retail trade of pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic articles(4.3 percentage points) and hypermarkets and supermarkets (2.4 percentage points). These two activities represented, respectively, 9.1% and 7.3% of the total revenue generated by the online retail sector in 2023. The retail trade of textiles, wearing apparel, footwear, and haberdashery saw the greatest decline (-3.0 percentage points) between 2019 and 2023, while the retail trade of information technology, communications, and household goods maintained the largest share of this revenue (61.4%) despite a 2.8 percentage point decline.
The retail trade of information technology, communications, and household goods generated 38.5% of its revenue online, the highest proportion of online sales among all activities. Retail sales of textiles, wearing apparel, footwear, and haberdashery, which in 2019 generated only 8.8% of its revenue online, increased to 13.4% in 2023, while retail sales of pharmaceuticals, toiletries, cosmetics, and medical, optical, and orthopedic articles nearly tripled, with online sales rising from 2.8% to 7.9% in the same period.
The IBGE structural analysis manager notes that the survey reflects how the pandemic influenced the shift in online revenue. "It was natural for people to return to shopping more in physical stores with the end of social distancing measures, but companies' adaptation to e- commerce and new consumer habits during the pandemic increased revenue through this channel, and that continued until 2023," says Miranda.




















