2022 Census
2022 Census identifies 2.4 million persons diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder in Brazil
May 23, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: May 23, 2025 10h47 PM

The 2022 Population Census identified 2.4 million persons diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), which corresponds to 1.2% of the Brazilian population. Prevalence was higher among men (1.5%) than among women (0.9%): 1.4 million men and 1.0 million women were diagnosed with autism by a healthcare professional. Among age groups, the highest prevalence was that of persons aged 5 to 9 (2.6%).
Data come from “2022 Population Census: Persons with Disabilities and persons Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder – Preliminary Census results,” released today (23) by the IBGE. The release event will take place today at 10 am, at the Brazilian Bar Association - Rio Grande do Norte Sector, in Natal (RN). The event will be streamed live on Digital IBGE. Read more about persons with disabilities.
“There is no great difference between Major Regions. The Central West has a slightly smaller proportion, with 1.1%, whereas the other ones have 1.2% of the population diagnosed with ASD. In absolute figures, as for the population overall, the Southeast concentrates the majority of persons, with a little more than one million persons diagnosed with autismo, followed by the Northeast, with 633 thousand; the South, with 348.4 thousand; the North, with 202 thousand and the Central West, with 180 thousand,” explained Raphael Alves, member of the technical team on persons with disabilities and persons diagnosed with autismo spectrum disorder in the Population Census.
Autism is highest among children and teenagers
As for age groups, the prevalence of autism diagnosis was highest among the youngest: 2.1% in the group aged 0 to 4; 2.6% for those aged 5 to 9; 1.9% in the group aged 10 to 14 and 1.3% for those aged 15 to 19. These percentages represent a total of 1.1 million persons with autism. In the other age groups, percentage ranged between 0.8% and 1.0%.
A joint analysis of sex and age data shows that boys aged 5 to 9 had the highest percentage of diagnoses: 3.8% of the male population in this age group, which is equivalent to 264.6 thousand persons. Among women in the same age group, the percentage was 1.3%, amounting to 86.3 thousand persons. A similar situation was observed in the group aged 0 to 4, with a prevalence of 2.9% among boys and of 1.2% among girls.
The prevalence of ASD was highest among men in all age groups up to the age of 44. For those aged 45 to 49, 55 to 59 and 70 and over, the percentages were equivalent between the sexes of birth. For those aged 50 to 54 and 60 to 69, prevalence among women was slightly higher than among men, with a difference of 0.1 percentage points.
ASD is prevalent among white persons
In the disaggregation by color or race, the highest percentage of persons with autism was found among White persons, with 1.3%, which is equivalent to 1.1 million persons. The lowest prevalence is found among Indigenous persons, with 0.9%, which represents 11.4 thousand persons. This percentage rises to 1% When persons of other color or race groups that consider themselves indigenous are included. Among Asians, 1,2% had a diagnosis of autism, corresponding to 10.3 thousand persons. About 221.7 thousand Black persons and 1.1 million brown persons suffer from ASD (autism spectrum disorder), representing 1.1% of each of these populations.
Population with autism has a highest schooling rate
The schooling rate of the population with autism (36.9%) was higher than that of the population overall (24.3%). This difference was more significant among men: 44.2% of the men with autism were studying, against 24.7% of the total. Among women, the schooling rates was 26.9% among those with autism, versus 24.0% in the total population.
“This difference is due to the highest concentration of the population with autism at younger ages, mainly those between 6 to 14 years of age, which have higher schooling rates and concentrate more than half of the population of students with autism,” Raphael explains.
Disaggregation by color or race estimated that, in 2022, 347.8 thousand white students had diagnosed autism, versus 344.4 thousand brown ones, 62.6 thousand black ones, 3.5 thousand indigenous ones and 2.4 thousand Asian ones. “By analyzing schooling rates, the same was observed in the analysis by sex: the rates among persons with autism were higher than among the population overall of all groups of color or race.”
The biggest difference was registered among schooling rates of white persons: 37.4% of persons with autism, against 23.5% of the total White population, that is, a ratio of 1.6 times. In the brown age group, the schooling rates of persons with autism (37.7%) also surpassed significantly the average of brown persons (25.9%). Among indigenous students, the difference was smaller: 36.0% among persons with autism, versus 34.3% of the total.
More than two thirds of the students with autism were attending primary school
The total of 760.8 thousand students aged 6 and over with autism in Brazil represented 1.7% of the total number of students in the range analyzed. The IBGE analyst highlights that “this percentage is higher than the proportion of persons diagnosed with autism in the general population (1.2%), a result that matches the higher prevalence of diagnosis among the population at school age, especially the youth.”
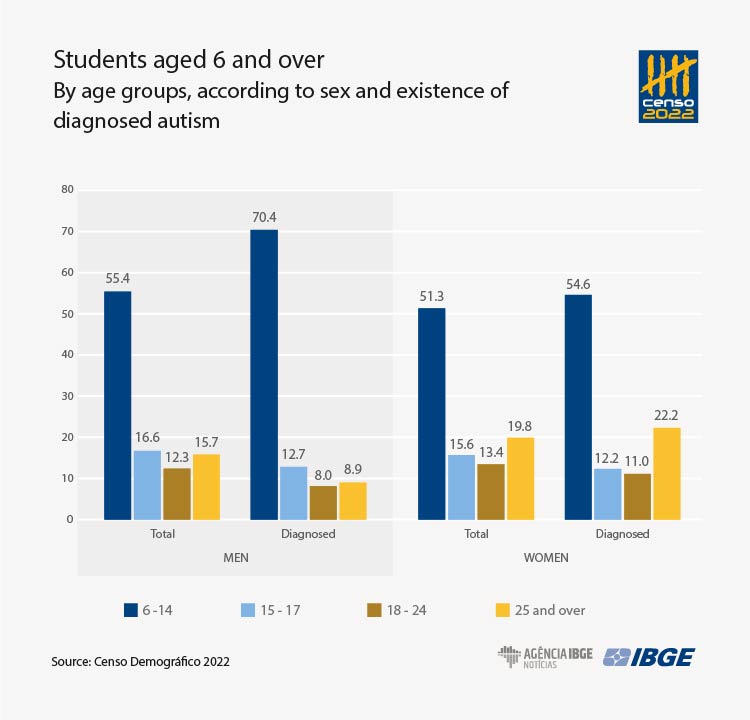
The group aged 6 to 14 concentrated the biggest share of students with this diagnosis: 70.4% of the men and 54.6% of the women with autism. In comparison, students in general in this age group represented 55% of the men and 51.3% of the women. Also, among persons with autism, this step of basic education presented a higher relative concentration than in the total student population. In the remaining age groups, the relationship is reversed: the percentages of students with autism are lower than the students overall.
More than two thirds of the students with autism were attending primary school
Most students with autism were enrolled in regular primary education, a total of 508 thousand persons, or 66.8% of the students with autism in Brazil. Regular high school concentrated 93.6 thousand students with autism and represented only 12.3% of those attending school. Data show that the school path of students with autism is concentrated in the early steps of basic education.
Considering the rate of students with autism in relation to the total number of students enrolled by course, literacy of youth and adults stands out with the highest percentage: 4.7% of the attendees reported this diagnosis. The proportion was even higher among students aged 15 to 17 (9.1%) and 18 to 24 (10.6%). Besides, 3.8% of the children attending day care centers had been diagnosed with ASD.
In higher education, this percentage drops to 0.8%, reflecting challenges faced by students with autism to remain and advance in their educational path, mainly before challenges related to access, curriculum adaptation and institutional support.
Almost half of the persons with diagnosed autism were in the group without schooling and with incomplete primary education
The percent distribution of persons aged 25 and over by level of schooling indicated that 46.1% of the persons with diagnosed autism were in the group without schooling and with incomplete primary school, whereas, in the population overall, this percentage was 35.2%. For other levels of schooling, the percentages of the population with autism were lower than those for the population overall. A highlight is the group with complete high school education and incomplete higher education, with 25.4% of the persons with autism versus 32.6% of the total population.
More about the survey
The 2022 Census presents, for the first time, information about autism, surveyed in the sample survey questionnaire by means of an item in which the informant reported if residents of the housing units had been diagnosed with autism by a healthcare professional. Data, disaggregated by sex, color or race, age groups and schooling of the population are presented for Brazil, Major Regions, States, Municipalities and other geographies based on Municipalities. The results can be accessed on the IBGE portal, on platforms such as SIDRA, and on the Census Overview, where they are accessible as interacrive maps.