RBMC
IBGE starts operating six new stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring and publishes time series of geodetic networks
December 15, 2023 10h00 AM | Last Updated: December 19, 2023 02h25 AM
Highlights
- Six new stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring of the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) started to operate in the following municipalities: Blumenau (SC), Cascavel (PR), Guajará-Mirim (RO), Guaíra (PR), Irecê (BA) and Resende (RJ).
- Currently, the IBGE has 147 RBMC and under the responsibility of the IBGE’s Geodesy Department.
- The updated time series for the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring of the GNSS Systems - RBMC and the Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network - RMPG have also been published today.
- The consolidated time series for the RPMG are updated every year and the change in average sea level is published here under the section “Data Analysis”.
- The IBGE has also announced today a group of new gravimetric stations (EEGG) which have been incorporated into the Brazilian Geodetic System (SGB) throughout 2023.
- The geodetic stations form the geodetic reference networks that compose the SGB.
- RBMC now has 53 stations that collect and publish GNSS data with a monitoring interval of 1 second.
- Another service rendered by the Geodesy Department is RBMC-IP, which allows real-time georeferencing using the Internet.
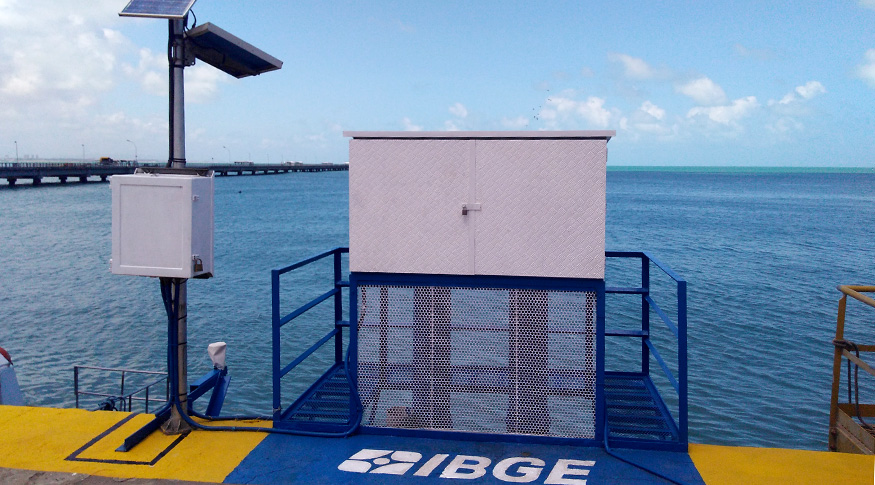

The IBGE started operating six mew stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring (RBMC) of GNSS systems for accurate georeferencing installed in the following municipalities: Blumenau (SC), Cascavel (PR), Guajará-Mirim (RO), Guaíra (PR), Irecê (BA) and Resende (RJ). The Institute has also published the updated time series of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring of GNSS Systems.
With these new additions, RBMC now has 147 stations. The operation and maintenance of RBMC stations is a duty of the IBGE’s Geodesy Department, in partnership with State Superintendencies and public institutions. The GNSS data made available daily on the IBGE website are public and free, being used in activities such as the demarcation of urban and rural property, precision agriculture and studies about sea level variation on the coast.
About the RBMC, Sonia Costa, Geodesy Coordinator for the IBGE explains that “GNSS data are used by a number of professionals, topographers, mainly, who conduct surveys not only aiming at the delimitation of rural and urban land, and by persons working in electricity, water and telephone concessionaires, among other activities in our economy that require accurate georeferencing.”
Since 2005, all geoinformation produced in Brazil must be associated to SIRGAS2000, a geodetic reference officially adopted by means of theResolução do Presidente (RPR) do IBGE Nº 1/2005. The access to this reference, and its monitoring, take place by means of geodetic reference network, which, in the case of SIRGAS2000 is constituted by the RBMC.
“The RBMC stations are references, being used with the purpose of playing the role of an origin or start, that is, we provide GNSS data and coordinates so that the user, in this case, a topographer, will need only one piece of equipment, because the other one is at the RBMC. station. We publish these data daily and have a target number of publications per month.”
Since 2017, with the inclusion of RBMC as one of the strategic projects of the institution, the stations have been paid special attention to regarding modernization of equipment, for, besides tracking the satellites of GNS and GLONASS constellations, the equipment also tracks the signals transmitted by satellites of Galileo (European system) and Beidou (Chinese System) constellations, as in four of the six new stations.
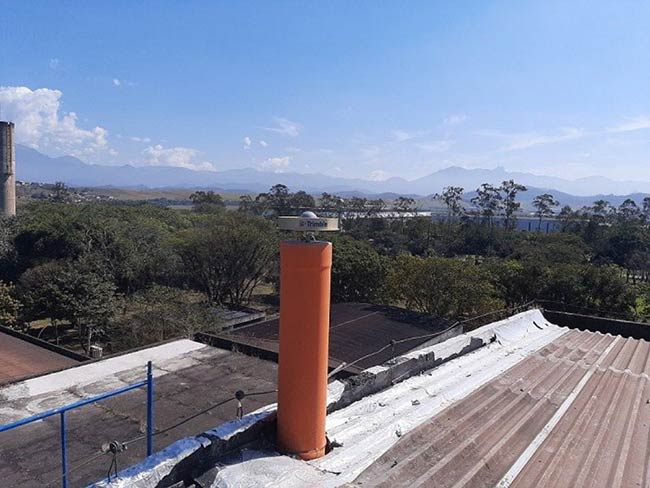

As part of the strategic Network Expansion project, new stations were established in 2023, and other improvements were made. (RBMC station in Resende, RJ)
Also, the new equipment has more storage capacity, and allows the issuing of files with a collection interval of 1 second, besides daily files of 15 seconds, an improvement that had been implemented since 2018. As a result, the RBMC now has 53 stations that collect and publish 1-second GNSS data. The customized tool for download of data available here, makes it possible for users to obtain a mass volume of data in a more user-friendly manner, according to their necessities.
Another example of a service rendered the the Geodesy Department is RBMC-IP, which allows real-time georeferencing using the Internet, resulting in centimeter-precise coordinates as long as the user is within a 30km maximum distance from a network station.
Time series of coordinates
Geodesy is the science that deals with the methods of precise position measuring and mapping of the Earth's surface. In line with this new concept of geodesy, the two active geodetic networks operated by the IBGE have been monitoring three-dimensional variational data that occur over a point on the Earth's surface, as well as the variations that occur at sea level , thus producing respective time series.
The IBGE has also released updated time series of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring of GNSS Systems (RBMC) and the Permanent Tide Gauge Network for Geodesy (RMPG). As part of the RBMC's operational activities, the daily updates of GNSS data enable the assessment of their quality and the attainment of time series of the coordinates.
“The equipment we use in RBMC is so accurate that we can monitor or estimate the variation of coordinates over time. This is what we call the time series of the coordinates. By calculating the coordinate obtained from the daily GNSS data, we can estimate this variation over time, and the quality is associated with an increase of the number of satellites, so we can improve the positioning accuracy and also provide greater reliability of results way faster" explained Sonia Costa.
All the RBMC stations are part of the Geocentric Reference System for the Americas SIRGAS, the result of a collaboration between American countries that provide the data from their continuously operating GNSS stations, which is one of the most accurate geodetic networks in the world. By means of a weekly processing of this data, it is possible to monitor, in a continuous way, the coordinates of the GNSS stations, identifying any displacements observed locally or regionally, such as the continuous movement of tectonic plates and/or those resulting from earthquakes. These movements or variations are represented through the time series of the coordinates, released here.
The consolidated time series of RMPG are updated annually in accordance with the criteria adopted in the report "Monitoring of the change of average Sea Level in Stations of the Permanent Geodetic Tide Gauge Network – RMPG 2001–2020". The single series for each station is generated by daily data made available by the IBGE on its website, with the necessary corrections of instrumental failures and reference height of sensors (offset). The time series of the variation of the average sea level is released here in the 'Data Analysis' section.
Set of Gravimetric Geodetic Station (EEGG) published in the Geodetic Database (BDG)
The IBGE releases today (15) a set of new gravimetric stations (EEGG) that have been incorporated into the Brazilian Geodetic System Network (BDG) during the year 2023. The information is released and available here to users of Geodetic Database - BDG. .
Measured since the 1940s, following a 5' x 5' grid or the direction of the roads (level references), materialized on the land or not, the IBGE’s EEGG are one of the components of the Brazilian Geodetic System Network (BDG).
Due to the improvements that such measurements have brought to the altimetric component since the last adjustment of RAAP – Realt2018, by incorporating the physical representation of a water masses flow, this activity is crucial for infrastructure activities in the country, such as territorial planning, construction of roads, bridges, dams, precision farming and utilities (energy, gas and basic sanitation).
Furthermore, by serving as a basis for development of the model for converting geometric altitudes, such as Mapgeo1994, Mapgeo2010, Mapgeo2015, and the latest hgeoHNOR2020, the EEGG enables the user community of GNSS equipment to obtain altitudes with respect to Earth's gravitational field. For further information about the New High Altitude Conversion – hgeoHNOR2020 please refer to this link.




















