2022 Census
2022 Census: Brazil has 14.4 million persons with disabilities
May 23, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: May 25, 2025 08h51 PM
Highlights
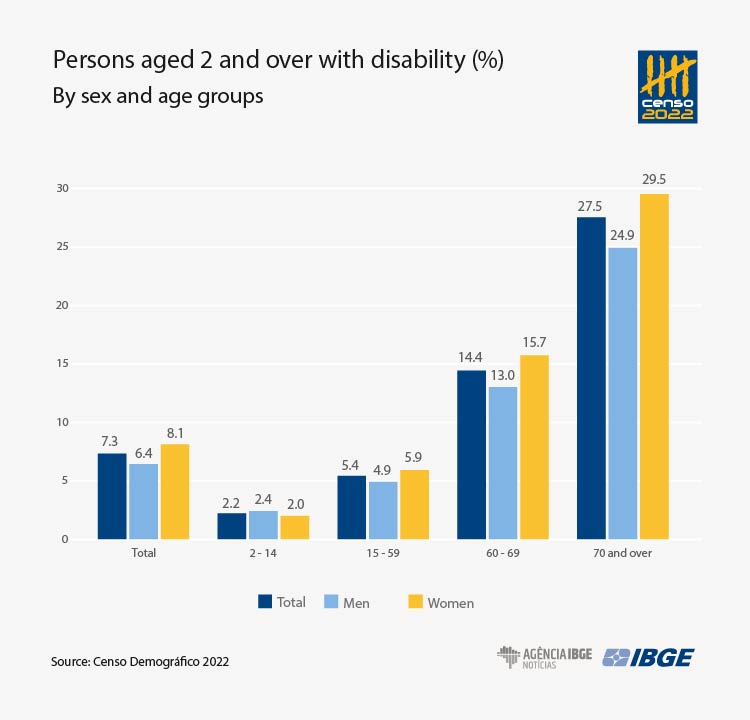
- In 2022, among the 198.3 million persons aged 2 and over in the country, 14.4 million (or 7.3%) were persons with disabilities. The number of women with disabilities (8.3 million) surpassed that of men in the same condition (6.1 million).
- Whereas 2.2% of the population aged 2 to 14 had some type of disability, in the group aged 15 to 59 the percentage rises to 5.4% and reaches 27.5% among persons aged 70 and over.
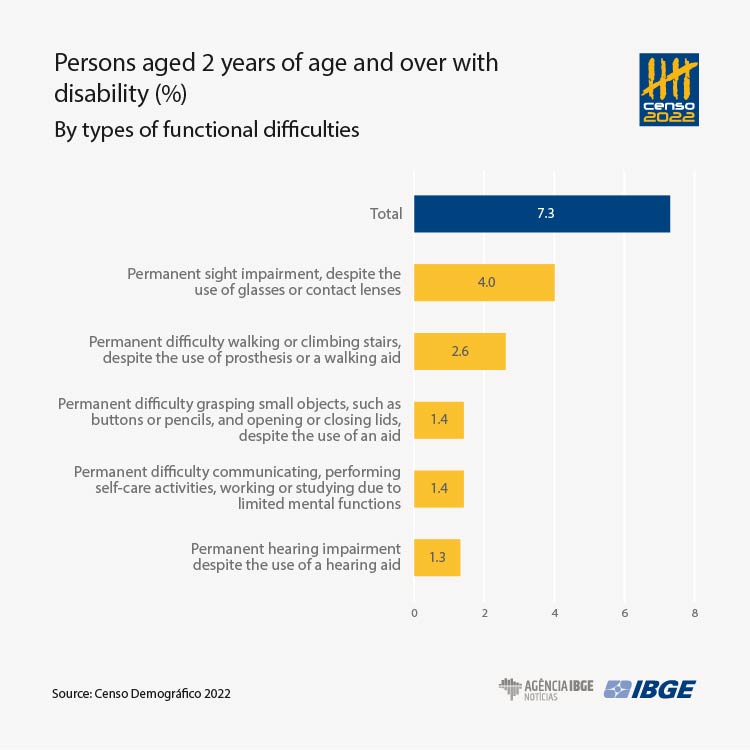
- As for the 14.4 million persons with disability in the country, 7.9 million had difficulty seeing, being followed by persons with difficulty walking or climbing up stairs (5.2 million persons), grasping small objects or opening and closing lids (2.7 million) and hearing (2.6 million).
- in Brazil, 2.0% of the population had two or more functional difficulties.
- in 16.0% of the enumerated housing units, there was at least one resident with disability. The Northeast recorded the highest percentage (19.5%), followed by the North (17.8%), the Southeast (14.7%), the Central West (14.3%) and the South (14.1%).
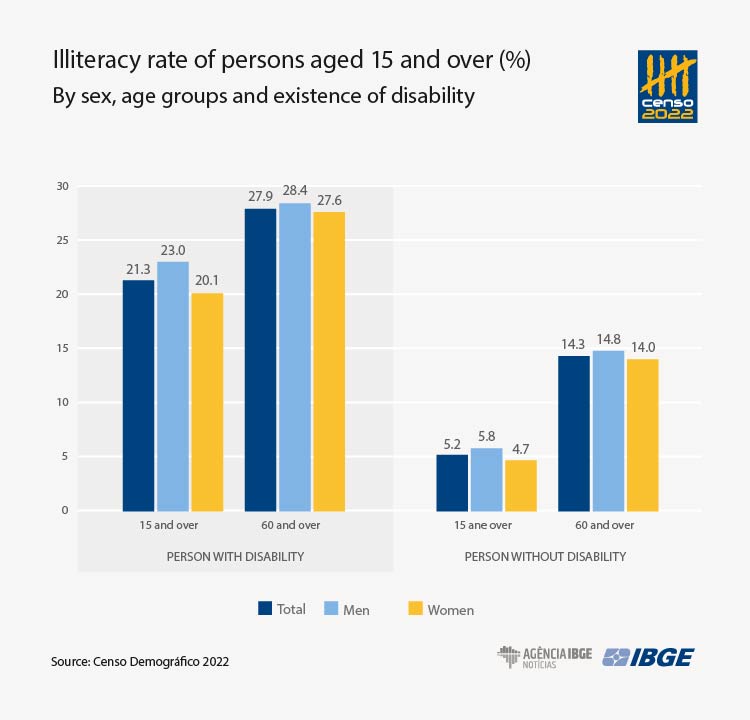
- In 2022, among persons aged 15 and over with disability, 2.9 million were illiterate. That corresponds to an illiteracy rate of 21.3%, or four times the illiteracy rate of persons without disability (5.2%).
- in Brazil, 63.1% of the persons aged 25 and over with disabilities did not have schooling or primary school education. among persons without disabilities, this proportion was almost half as that (32.3%).
- In 2022, only 7.4% of the persons with disabilities had finished higher education, versus 19.5% of the persons without disabilities.
Preliminary results of the 2022 Census show that Brazil has 14.4 million persons with disabilities, which corresponds to 7.3% of the 198.3 million persons aged 2 and over in the population. Elderly persons aged 60 and over made up 45.4% of persons with disabilities, whereas, in the population without disabilities they were 14.0%. Women with disabilities were 8.3 million and men, 6.1 million. In all Major Regions, women with disabilities were more numerous than men in the same conditions. That can be associated to the higher female longevity in the Brazilian population.
Data are found in the publication “2022 Population Census: Persons with Disability and persons Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum - Preliminary sample results,” released today (23) by the IBGE. The release event took place today, starting at 10 am, at the Brazilian Bar Association - Rio Grande do Norte Sector, in Natal (RN), with live stream on Digital IBGE. See also the report on the population with autism.
Over the years, Brazil has witnessed discussions promoted by international cooperation bodies about ways of collecting disability data by means of household surveys. Since 2010, the IBGE has adopted the survey of functional domains, a new approach to disability recommended by the Group of Washington, adapted to the Brazilian reality. Thus, although disability-related issues are found in the Censuses of 1991, 2010 and 2022, and in the National Survey of Health (PNS) and in Continuous PNAD, there are methodological differences between them, which makes comparisons impossible.
In the nine states of the Northeast Region, the percentages of persons with disabilities surpassed the national average (7.3%). Alagoas had the biggest proportion of persons with disabilities in the country (9.6%) in its population. Piauí (9.3%), Ceará and Pernambuco (both with 8.9%) followed. Out of the Northeast, Rio de Janeiro was the state with the biggest proportion (7.4%). The smallest proportion of persons with disabilities were found in Roraima (5.6%), Mato Grosso (5.7%) and Santa Catarina (6.0%).
Luciana dos Santos, analyst at the IBGE, observes: “Although it is not yet possible to assess, based on the 2022 Census data, the relationship between the occurrence of disability and income, studies indicate a correlation between the prevalence of disability with lower access to basic services, educatio, health nd quality of living in general. In this context, the Northeast Region, historically characterized by low human developement indexes, ends up being more vulnerable to circumstances that can cause disability, such as malnutrition, lack of access to healthcare, etc. That is, the higher incidence of disability in the Northeast reflects the social and economic inequalities in that Major Region.”
More than 1/4 of the persons aged 70 and over have some type of disability
The prevalence of disability increases with age. Whereas only 2.2% of the population aged 2 to 14 had some type of disability, the percentage rose to 5.4% among adults aged 15 to 59 years of age and reaches 27.5% among persons aged 70 and over.
Among persons with disabilities, 32.8% were aged 60 to 79, versus 12.5% of persons without disabilities. In the group aged 80 and over, 12.6% were persons with disabilities and only 1.5% were persons without disabilities.
Sight impairment affects 7.9 million persons in the country
Considering the total number of persons with disabilities (14.4 million), the most frequent functional difficulty was sight impairment, despite the use of glasses or contact lenses, which reached about 7.9 million persons. It was followed by difficulty in walking or climbing up stairs, despite the use of a prosthesis or a walking aid, reaching a total of 5.2 million persons.
The functional difficulty related to manual dexterity (the ability to grasp objects or to open or close lids) and the functional difficulty relative to mental functions (with effects on communication self-care, labor or studies reached 2.7 million persons each. Hearing impairment, despite the use of a hearing aid, reached 2.6 million persons.
About 2.0% of the population in the country aged 2 and over had one or more functional impairment. Among Major Regions, the highest percentage (2.4%) of persons with disability with two or more functional difficulties was found in the Northeast Region.
7.9% of the Indigenous persons aged 2 and over have some type of disability
Among the 1.6 million Indigenous persons aged 2 and over in the country, 131 thousand or (or 7.9%) had some type of disability, considering criteria of color or race and belonging. Although the biggest share of the Indigenous population in the country (43.8%) lives in the North Region, the Northeast had the biggest proportion of indigenous persons with disabilities (42.4%), followed by the North Region (33.5%).
In the Indigenous population, 7.9% were persons without disabilities, but among Indigenous persons aged 65 and over, this percentage reached 30.6%. In the Indigenous population in this age group, 33.3% of the women and 27.2% of the men had some type of disability.
According to color or race categories, the 2022 Census showed that most of the persons with disabilities in Brazil declared to be brown (6.4 million) or white (6.1 million). This group was followed by black persons with disabilities, with approximately 1.8 million; Indigenous (considering the color or race aspect only) with 78 thousand; and Asians, with 55 thousand.
19.3% of the housing units in the country without a bathroom had at least a resident with disabilities
In 16.0% of the occupied private housing units enumerated in the country had at least one resident, either a grown-up or child, with disabilities. The Northeast Region had the highest percentage of housing units with at least one resident with disabilities (19.5%), followed by the North (17.8%), Southeast (14.7%), Central West (14.3%) and South (14.1%).
In housing units with an exclusive bathroom, 15.9% had at least one resident with disability. This percentage was higher in the housing units that have only a bathroom for collective use by more than one housing unit (18,5%) and even higher in housing units without a bathroom of toilet (19.3%).
Among the housing units connected to the public water supply system and that used it as the main form of supply, 15.7% had at least one resident with disability. In housing units not connected to the public system, 18.0% had at least one resident with disabilities.
Population with disabilities is far from the PNE target for illiteracy
To guide public policies in the field of education and promote improvements in educational indicators in the country, Target 9 of the National Plan of Education (PNE) established the reduction of illiteracy among persons aged 15 and over to 6.5% until 2015 and the eradication of illiteracy until 2024.
In 2022, in the population aged 15 and over, there were 2.9 million persons with disabilities and illiterate, which represents an illiteracy rate of 21.3%. Among persons without disabilities of the same age bracket, 7;8 million were illiterate, corresponding to an illiteracy rate of 5.2%.
Almost half (48.0%) of the persons with disabilities, and illiterate, lived in the Northeast, whereas 27.7% lived in the Southeast. Piauí (38.8%), Alagoas (36.8) and Paraíba (34.6%) recorded the highest illiteracy rates among persons with disabilities, whereas the lowest rates were in Santa Catarina (11.6%), Federal District (11.8%) and Rio de Janeiro (12.1%).
The 2022 Census shows a scenario of deep inequalities for the population with disabilities. In this age group, the literacy rate of persons aged 15 and over (21.3%) was more than three times above the established target. Despite the progress in the population overall, non-compliance with the PNE target for this segment shows that persons with disabilities remain marginal to educational advances.
“However, there were significant advances in the literacy of persons with disability, evidenced by the illiteracy rate aged 15 to 17, which is 11.2% - an index 2.5 times below that of elderly persons aged 60 and over, whose rate reaches 27.9%. Despite this progress, there are still relevant barriers Against the educational inclusion of this population,” the analyst highlighted.
Persons with disabilities have lower access to Education
In Brazil, 63.1% of the persons aged 25 and over with disabilities did not finish primary education, whereas, among persons without disabilities, this proportion was 32.3%. On the other extreme, only 7.4% of the persons with disabilities finished higher education, versus 19.5% among persons without disabilities. Also, 25.2% of the persons with disabilities completed compulsory basic education (at least high school level). Among persons without disabilities, this proportion was more than double: 53.4%.
Among persons without disabilities, 56.4% of the women and 50.1% of the men had completed basic education – a difference of 6.3 percentage points. Among persons with disabilities, 26.2% of the women reached that level, against 23.7% of men, showing a lower difference of 2.5 percentage points.
In 2022, approximately 1.6 million persons aged 6 and over with disabilities were attending school at any level. The schooling rates (proportion of students at a given age bracket) among children aged 6 to 14 were 98.4% for persons without disabilities and 92.6% for those with disabilities.
However, from the age of 15 on, a drop in school attendance is observed, especially of persons with disabilities. In the group aged 15 to 17, 85.5% of the persons without disabilities were in school, against 79.4% of those with disabilities.
More about the survey
The 2022 Census - Persons with Disabilities and persons Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) - Preliminary sample results presents sociodemographic and educational profiles of persons aged 2 and over with disability and of persons diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder by a healthcare professional (ASD).
In compliance with guidelines established by the Washington Group on Disability Statistics, the 2022 Population Census introduced items aimed at the identification of five domains of functional difficulties: seeing, hearing, Mobility of lower limbs, fine motor skills and cognition and communication.
OsThe indicators are detailed for Brazil, Major Regions, Federation Units and municipalities, being disaggregated by color or race, sex and age groups of residents. The results can be accessed on the IBGE website and on platforms such as SIDRA and the Census Overview, where data can also be visible as interactive maps.