Women dedicate more hours to household tasks and care of persons, even in same occupational situation as men
April 26, 2019 10h00 AM | Last Updated: May 02, 2019 10h22 AM
Among the persons aged 14 years and over, 87.0% (147.5 million) carried out household tasks and/or care of persons in 2018. Women not employed in the labor market dedicated 23.8 hours to these activities, whereas men in the same situation dedicated 12.0 hours. The difference was also big between employed women (18.5 hours) and men (10.3 hours).
The achievement rate of household tasks for women (92.2%) remained higher than that of men (78.2%), though this difference (14 percentage points (p.p.)) had been higher in 2016 (17.9 p.p.) and in 2017 (15.3 p.p.).
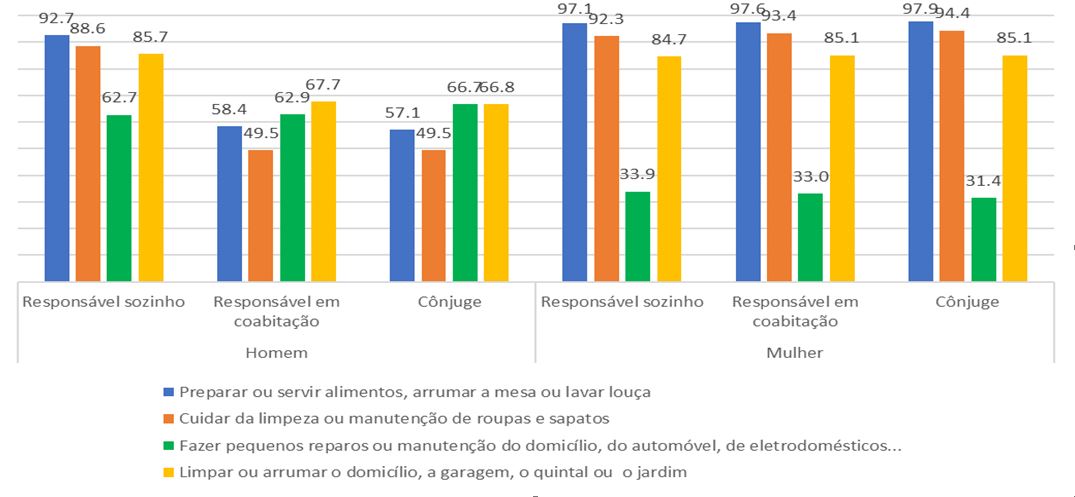
Cooking was the activity that registered the biggest difference between sexes (34.7 p.p.). The achievement rate of this activity among men (92.7%) and women living alone was close (97.1%). On the other hand, this percentage was quite smaller among men in cohabitation in the condition of either responsible for the household (58.4%) or spouse (57.1%) than among women in the same conditions (97.6% and 97.9%, respectively).
The percentage of women (37.0%) who took care of persons remained higher than that of men (26.1%). Men with either no education or incomplete primary school recorded the lowest achievement rate (22.0%). The age bracket between 25 and 49 years posted the highest percentage both
for men (37.0%) and for women (49.8%).
Among the persons aged 14 years and over, 7.2 million (4.3%) carried out voluntary work in the reference week of the survey. Of this total, 48.4% volunteered four or more times per month, whereas 15.6% did it either casually or without a specific frequency. They dedicated an average time of 6.5 weekly hours.
The production for their own consumption was accomplished by 13.0 million persons at working age (7.7%). This rate had been increasing since 2016 (6.3%). Among those who produced for their own consumption, most of them (76.7%) carried out the activity of cropping, fishing, hunting and animal breeding.
These are some of the highlights of the Other Forms of Work supplement of the 2018 Continuous PNAD. The support material of the survey is on this page.
In 2018, 147.5 million persons aged 14 years and over carried out domestic tasks and/or care of persons, either in their own households or in the household of relatives. This figure corresponded to 87.0% of the population at working age. It increased 3.1 million persons over 2017, when the achievement rate was 86.0%.
The achievement rate of domestic tasks and/or care of persons was quite higher among women (93.0%) than among men (80.4%). In addition, the weekly hours spent by women (21.3 hours) in these activities were, on average, nearly twice those spent by men (10.9 hours).
Women dedicated more hours to household tasks and care of persons, even in same occupational situation as men. As a result, they eventually had less time available for paid work.
| Average hours dedicated to household tasks and/or care of persons | |
|---|---|
| Employed man | 10.3 |
| Employed woman | 18.5 |
| Unemployed man | 12.0 |
| Unemployed woman | 23.8 |
| Average hours effectively worked in all jobs | |
| Man who carried out household task and/or care of persons | 39.9 |
| Woman who carried out household task and/or care of persons | 34.8 |
| Man who did not carry out household task and/or care of persons | 39.0 |
| Woman who did not carry out household task and/or care of persons | 36.0 |
Household tasks: achievement rate of women remains higher that that of men, though difference decreases
In 2018, 85.6% of persons aged 14 years and over carried out domestic tasks either in their own households or in the household of relatives. This percentage corresponded to 145.1 million persons, an increase of 3.3 millions compared with 2017 (84.4%).
The increase in the rate was higher for men (1.8 p.p.) than for women (0.5 p.p.), though the percentage of women (92.2%) remained higher than that of men (78.2%). Yet, this difference (14 p.p.) was even higher in 2016 (17.9 p.p.) and in 2017 (15.3 p.p.), which pointed out to a reduction trend.
The achievement rate of women was quite high, especially in the condition of spouse (97.3%) or responsible for the household (95.3%). Among men, the highest rate was that of those responsible for the household (86.5%), followed by spouses (82.4%). The condition of son present the lowest rates, either for men (65.0%) or women (84.4%), though the men´s rate in this condition was that mostly increase (2.6 p.p.).
The Central-West region (88.6%) registered the highest achievement rate of household tasks and the Northeast (81.0%), the lowest one. The biggest difference between the achievement rates for men and women was in the Northeast (20.9 p.p.) and the lowest one, in the South (10.1 p.p.).
Achievement rate of household tasks increases with schooling level
Despite the highest increase among the age group between 14 and 24 years (2.4 p.p.), the accomplishment of household tasks remained higher among adults aged between 25 and 49 years (89.4%). The rate also remained higher among the employed persons (88.0%) than among those unemployed (82.8%). Such difference was not quite relevant among women (5 p.p.) as it was among men (11.9 p.p.), showing a trace of the double shift of women.
90.1% of the persons with complete higher education carried out domestic tasks, whereas the rate was 82.2% among those without education or with incomplete primary school. The accomplishment of household tasks increased with the increase of schooling level, though the highest increase in this period was in the complete secondary school and incomplete higher education: from 86.3% (2017) to 88.0% (2018).
The difference in the accomplishment of household tasks by schooling level was lower among women: 90.1% (without education or with incomplete primary school) and 93.4% (complete higher education). On the other hand, the difference was more relevant among men: 74.3% (without education or with incomplete primary school) and 85.4% (complete higher education).
Men in cohabitation in the condition of responsible or spouse carry out less household tasks than women in these same conditions.
The survey also showed the percentage of persons who carried out domestic tasks in their own households by activity type. "Making small repairs or maintenance in the household, car, household appliances, etc." was the only activity in which women (30.6%) recorded a lower achievement rate than men (59.2%).
Among the activities in which the rate was higher for women, cooking (34.7 p.p.), washing clothes and footwear (36.9 p.p.) and cleaning the household (13.9 p.p.) were the three ones with the biggest differences between the sexes. In each one of them, the rate for men responsible for the household who live alone was quite close to that for women. Among the men in cohabitation in the condition of responsible or spouse, the percentage was quite lower than that of women in these same conditions, possibly pointing out the sexual division of the work at home.
Care of persons: Achievement rate is 37% for women and
26.1% for men
In 2018, 54.0 million persons aged 14 years and over took care of children, seniors or sick persons – either residents in the household or relatives not living in the household –, which corresponded to a rate of 31.8%. It increased 974 thousand persons in relation to 2017 (31.5%). The accomplishment of care of persons was higher in the North (38.0%) and lower in the South (30.7%).
Between 2017 and 2018, the rate for women remained 37.0% and that of men changed from 25.6% to 26.1%. Nevertheless, the difference between sexes remained significant (10.9 p.p.). Women in the North Region posted the highest rate (44.9%) and men in the Northeast, the lowest one (24.3%).
Among the age groups under analysis, the highest achievement rate was that of persons aged between 25 and 49 years (43.7%), an age bracket in which the presence of children in the household was most likely. The rate was 26.5% among the youngsters aged between 14 and 24 years, while that for those older than 49 years, 19.6%. Women aged between 25 and 49 years registered the highest achievement rate (49.8%) and men aged 50 years and over, the lowest one (15.8%).
The accomplishment of care of persons was bigger among those who declared themselves as brown (33.7%), followed by those declared as black (32.4%) and white (29.7%). The difference between the rate for brown men in relation to white men was of 1.6 p.p., whereas it was 6.5 p.p. among brown and white women.
Men without education or with incomplete primary school registered the lowest achievement rate of care of persons
Among the persons without education or with incomplete primary school, 27.0% took care of persons, whereas the percentage was 34.0% among those with complete higher education. The trend of increasing the rate with the increase in the schooling level was marked by the behavior of men. Among those with complete higher education, the rate was 30.6% and among those without education or with incomplete primary school, 22.0%.
In the case of women, the highest percentage occurred among those with complete primary school and incomplete secondary school (41.1%), followed by women with complete secondary school and incomplete higher education (40.6%) and dropping to 36.4% among those with complete higher education.
Care of persons was bigger among the employed persons (34.0%) than among those unemployed (29.3%). The difference was quite bigger for men (11.7 p.p.) than for women (3.2 p.p.).
The care of household residents was predominantly destined to children and teenagers up to 14 years of age: 50.7% for residents aged between 0 and 5 years and 51.1%, between 6 and 14 years.
The most frequent activity was the monitoring inside the household, both among men (87.9%) and women (91.6%). Conversely, assistance with educational activities recorded the lowest percentage: 60.7% for men and 72.0% for women. The highest differences of percentage between men and women were in the assistance with personal care (18.6 p.p.) and assistance with educational activities (11.3 p.p.).
Voluntary work: achievement rate increases with schooling level
In 2018, 7.2 million persons aged 14 years and over carried out voluntary work in the reference week of the survey, which corresponded to 4.3% of that population. This percentage was higher among women (5.0%) and among employed persons (4.6%). In 2017, the achievement rate of voluntary work was 4.4%.
In general, the voluntary work increased with age, except in the North and Northeast regions, where the highest rate occurred among persons aged between 25 and 49 years (5.5% and 3.5%, respectively). Persons aged 50 years and over in the South Region posted the highest achievement rate (6.0%), while youngsters aged between 14 and 24 years in the Northeast Region registered the lowest one (2.3%).
The accomplishment of voluntary work increased with schooling level. The rate was 2.9% for persons without education or with incomplete primary school and 8.0% for those with complete higher education.
Average time dedicated to voluntary work is of 6.5 weekly hours
The voluntary work can be carried out either individually or through enterprises, organizations or institutions. The proportion of persons who carried it out individually was small, though it had been increasing year after year: 8.4% in 2016; 9.0% in 2017 and 9.8% in 2018.
Among the persons who carried out voluntary work, 79.9% did it in religious congregations, unions, condos, political parties, schools, hospitals or asylums and 13.0% in associations of residents, sports associations, NGOs, supporting groups or other organizations, considering that persons could accomplish them in more than one place.
Concerning frequency, 48.4% stated that they accomplished it four or more times per month, whereas 15.6% did it casually or without a certain frequency. They dedicated an average time of 6.5 weekly hours.
Production for own consumption: rate has been increasing year after year
In 2018, 13.0 million persons aged 14 years and over produced for their own consumption. The rate had been increasing since 2016, when it recorded 6.3%, changed to 7.3% in 2017 and reached 7.7% in 2018.
This rate was higher among men (8.4%) and among unemployed persons (8.7%), which were the categories that mostly increased between 2017 and 2018 (0.5 p.p.).
The production for own consumption increased with age. The percentage was 3.4% among youngsters aged between 14 and 24 years and among those aged 50 years and over (11.0%). The Northeast (14.8%) and South (14.7%) regions posted the highest achievement rates for persons aged 50 years and over. This age group also registered the biggest increase from one year to the other, mostly among men (0.9 p.p.).
The achievement rate of production for own consumption has an inverse relationship with schooling level: 13.2% among persons without education or with incomplete primary school and 3.1% among those with complete higher education.
The rate increased in every schooling level from one year to the other (0.4 p.p. in each level). Separating by sex, the biggest increase occurred among men without education or with incomplete primary school (0.9 p.p.).
Cropping, fishing, hunting and livestock prevail as activities for own consumption
In regard to the activities for own consumption, 76.7% of the persons stated that they carried out cropping, fishing, hunting and animal breeding; 14.5%, production of coal, chopping or collection of firewood, straw or other material; 13.7%, manufacture of footwork, clothes, furniture, tiles, food or other products and 8.0%, construction of buildings, rooms, wells or other works for their own use. A person could have done more than one type of activity. In relation to 2017, only the activity group of "production of coal, chopping and collection of firewood, straw or other material" reduced (-2.3 p.p.).
Manufacture of footwear, clothes, furniture, tiles, food or other products was the only group in which women (27.5%) posted a higher percentage than men (1.0%), as well as presented the highest percentage difference between sexes (26.5 p.p.).
Having registered the highest position in every region, the percentage of production of the group of cropping, fishing, hunting and animal breeding changed from 66.3% (Southeast) to 82.2% (North). The group of production of coal, chopping or collection of firewood, straw or other material was more present in the Northeast (20.2%) than in the Central-West (7.8%).
On the other hand, the group of manufacture of footwear, clothes, furniture, tiles, food or other products recorded a lower percentage in the North (8.5%) and Northeast (7.1%) and a higher percentage in the Southeast Region (20.7%). The Southeast posted the highest percentage of persons constructing buildings, rooms, wells or other works (13.0%) and the Northeast Region, the lowest one (4.3%).
The average number of hours worked in construction was 13.4 hours and 4.3 weekly hours in the production of coal, chopping or collection of firewood, straw or other material. Cropping, fishing, hunting and animal breeding was the activity group with the highest difference of worked time between men and women (3.2 hours more for men).

