Continuous PNAD - ICT 2017: Internet reaches three of every four households in the country
December 20, 2018 10h00 AM | Last Updated: December 21, 2018 11h04 AM
The percentage of households that used the Internet rose from 69.3% to 74.9%, from 2016 to 2017, representing an increase of 5.6 percentage points. In this period, the proportion of households with landline telephones fell from 33.6% to 31.5%, while the presence of mobile phones increased from 92.6% to 93.2% of households. These are some of the data from Continuous PNAD ICT 2017, IBGE's household survey that investigates Internet and television access, as well as mobile phone ownership for personal use.
Of the 181.1 million persons aged 10 or older in the country, 69.8% accessed the Internet at least once in the three months prior to the survey. In absolute numbers, this contingent rose from 116.1 million to 126.3 million in the period. The highest percentage was in the 20-24 age group (88.4%). The proportion of the elderly (60 years old or older) who accessed the Internet rose from 24.7% (2016) to 31.1% (2017) and showed the largest proportional increase (25.9%) among the age groups analyzed by the survey.
From 2016 to 2017, the percentage of persons who accessed the Internet through mobile phones increased from 94.6% to 97.0%, and the share of television used for that purpose rose from 11.3% to 16.3%. Conversely, the rate of those who used desktop computers to access the Internet fell from 63.7% to 56.6%.
"Sending or receiving text, voice or picture messages by applications other than the email" was the purpose of network access indicated by 95.5% of Internet users. "Voice or video calls" was the purpose that presented the highest increase from 2016 (73.3%) to 2017 (83.8%).
The share of the population aged 10 and over that had mobile phones for personal use rose from 77.1% (2016) to 78.2% (2017). In the urban area, this percentage was 81.9% and, in rural areas, 55.8% in 2017.
In 96.7% of the country's 70.4 million households, there was a television set, of which 79.8% had a converter (integrated or adapted) to receive the digital open television signal. The percentage of households that were already receiving the signal grew
from 57.3% (2016) to 66.6% (2017) and the share of those who did not have any of the three conditions of access to the digital signal (converter, satellite dish or pay TV) fell from 10.3% (2016) to 6.2% (2017).
The support material of the Continuous PNAD - ICT is on the right of the page.
Internet reaches 74.9% of households in Brazil
From 2016 to 2017, the percentage of Internet use in households increased from 69.3% to 74.9%, or three out of every four Brazilian households. It was a leap of 5.6 percentage points in a year. In urban areas, this percentage increased from 75.0% to 80.1% and in the rural area, from 33.6% to 41.0%.
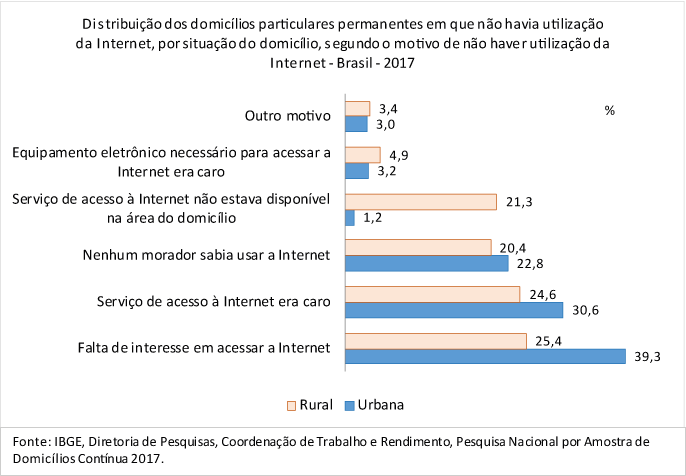
In the 17.7 million households where the Internet was not used during the reference period of the survey, the reasons indicated by the interviewees were: lack of interest in accessing the Internet (34.9%), expensive Internet access service (28.7%), lack of knowledge on how to use the Internet (22.0%), unavailable Internet access service in the household area (7.5%) and expensive electronic equipment to access the Internet (3.7%).
The unavailability of the Internet access service was the reason indicated in only 1.2% of the households in the urban area, against 21.3% of those in rural areas.
Of the 181.1 million persons aged 10 and older, 69.8% (126.3 million) accessed the Internet in the three months prior to the interview. This share was 64.7% (116.1 million) in 2016. In urban areas, this percentage increased from 70.0% to 74.8%, and from 32.6% to 39.0% in the rural area.
The 20-24 age group had the highest percentage of persons who accessed the Internet (88.4%) in the reference period and the elderly (60 years old and above), the lowest (31.1%).
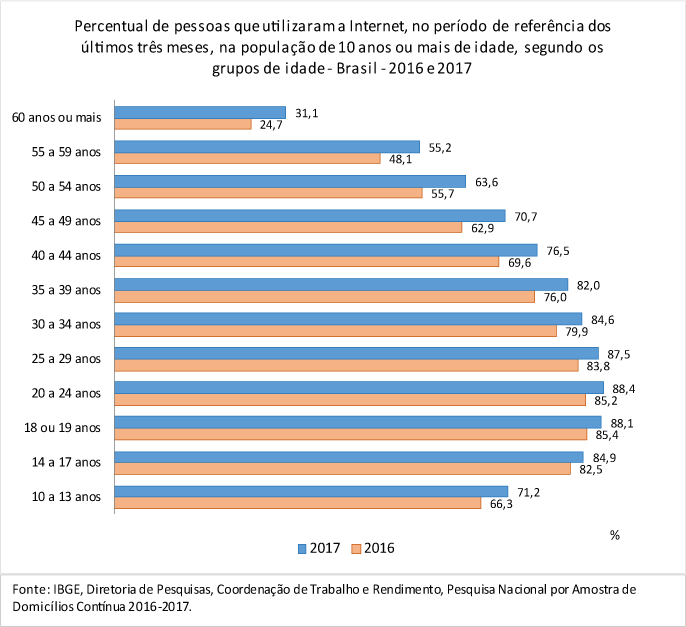
In the elderly population, the share that accessed the Internet rose from 24.7% (2016) to 31.1% (2017), showing the largest proportional increase (25.9%) among the age groups.
In the rural area, the percentage of women who accessed the Internet (41.9%) remained higher than that of men (36.3%). Among the regions, the distance between the percentage of internet access in urban and rural areas was large, with the highest inequality (69.6% in urban and 27.0% in rural areas) in the North.
The percentage of Internet use by the population aged 10 or older grows according to schooling: the lowest percentage of use was among the uneducated (11.2%) and the highest, among those with incomplete higher degree (97.7%) and with complete higher education (96.4%).
From 2016 to 2017, the percentage of persons using the Internet rose from 75.0% to 80.4% in the employed population and from 52.4% to 56.8% in the unemployed.
Mobile cell phones are means of Internet access for 97.0% of users
The percentage of persons aged 10 or older who accessed the Internet through mobile phones increased from 94.6% (2016) to 97.0% (2017) and the share of television users for that purpose increased from 11.3% (2016) to 16.3% (2017).
On the other hand, the percentage of persons using a personal computer for Internet access fell from 63.7% to 56.6%, a behavior similar to that of the tablets, whose rate of use fell from 16.4% to 14.3% in the period.
95.5% of users access the Internet to exchange message through apps
"Sending or receiving text, voice or picture messages by applications other than e-mail" was indicated by 95.5% of users as the purpose of access to the web. In 2016, this percentage was 94.2%. The purpose of "voice or video call" was the one that presented the largest increase from 2016 (73.3%) to 2017 (83.8%).
The percentage of people who used the Internet to "watch videos, including shows, series and movies" went from 76.4% to 81.8% in that period.
Among the purposes analyzed by the survey, the percentage of those who accessed the web to "send and receive emails" was the only one to decrease from 2016 (69.3%) to 2017 (66.1%).
The share of the population that used the dial-up connection was already insignificant in 2016 (0.9%) and became even smaller in 2017 (0.6%). The percentage of fixed broadband increased from 81.0% (2016) to 82.9% (2017) and remained above mobile broadband, which increased from 76.9% to 78.3% in that period.
The percentage that used the two types of broadband rose more sharply, from 2016 (58.3%) to 2017 (61.4%).
13.7% of those who do not access the Internet consider the service expensive
The major reasons pointed out by the 54.8 million persons aged 10 and over who did not use the Internet in the last three months were: not knowing how to use the Internet (38.5%), not having access to it (36.7%), and considering the Internet service was expensive (13.7%).
The percentage of persons with no interest in Internet access registered a notable difference between the urban (39.7%) and rural (29.3%) population. The unavailability of the Internet access service in the area was the reason indicated by 12.9% of the persons who did not use the web in the rural area, while in the urban area, it was 1.7%.
78.2% of the persons aged 10 or older had a cell phone for personal use
In the population aged 10 or older, the share that had cell phone for personal use went from 77.1% (2016) to 78.2% (2017). In 2017, in the urban area, this percentage was 81.9%, and, in rural area, 55.8%.
The percentage of persons with cell phones was lower among the population in the group of 10-13 years old (41.8%) and reached the largest participation in the age groups of 25-29 years old (88.8%) and of 30-34 years old (88.9%), gradually falling to 63.5% among the elderly (60 years old or older).
This indicator was 41.8% among the uneducated and 97.5% among those with complete higher education.
Of the 39.4 million persons who did not have a cell phone, 25.7% said they did not have the device because it was expensive; 23.2% reported to use someone else's cell phone; 21.3% claimed lack of interest in having one and 19.4% said they did not know how to use the device. The percentage of people who indicated that mobile cellular telephone service was not available in the places they used to attend was 8.2% in rural areas and only 0.4% in urban areas.
Mobiles present in 93.2% of the households
From 2016 to 2017, there was decrease in the percentage of households with a desktop computer (from 45.3% to 43.4%) and tablets (from 15.1% to 13.7%).
In 2017, 5.1% of households did not have a telephone, and in 2016, that percentage was 5.4%. The percentage of households with fixed telephones fell from 33.6% to 31.5% and those with mobile telephones rose from 92.6% to 93.2%. The share of households in which there was a fixed telephone only rose from 2.0% (2016) to 1.7% (2017).
In households with Internet, mobile access prevails
The cell phone was the most used equipment to access the Internet at the households (98.7% of the households where there was Internet use). In 2016, this percentage was at 97.2%. The percentage of households that only used mobile phones to access the web also increased, from 38.6% (2016) to 43.3% (2017).
The percentage of households with access to the Internet through a personal computer dropped from 57.8% in 2016 to 52.3% in 2017. The percentage of households where the microcomputer was the only means of accessing the Internet also decreased: from 2.3 % (2016) to 0.9% (2017).
The percentage of households that used the Internet and accessed it through TV rose from 11.7% to 16.1%. On the other hand, tablet access was present in 15.5% of the households where the web was used in 2017 and 17.8% in the previous year.
Mobile broadband was in 78.5% of households with Internet
In the 52.7 million households in the country that accessed the Internet, the share that used dial-up connections was irrelevant, falling from 0.6% (2016) to 0.4% (2017).
The percentage of those using mobile broadband (3G or 4G) increased from 77.3% to 78.5%, and from those using fixed broadband, from 71.4% to 73.5%.
The use of both types of broadband grew from 49.1% (2016) to 52.2% (2017). On the other hand, there was a small drop in the percentage of households in which there was only use of mobile broadband (from 26.7% to 25.2%) and households that only had fixed broadband (21.2% to 20.3%).
In the North, the percentage of households with Internet access through fixed broadband stood at 48.8%, far below the results found in the other regions, from 74.2% (Northeast) to 77.2% ( South). In relation to households with mobile broadband, the lowest percentage was in the Northeast region (63.8%) and the remaining ones were between 78.6% (South) and 88.7% (North).
66.6% of the households with TV received the digital signal through converters
Of the 70.4 million permanent private households in the country, 3.3% had no television. This percentage was 2.8% in 2016. The share of households with thin-screen television rose from 65.0% to 69.7% and that of tube television fell from 44.9% to 38.9% . In 57.8% of households there was only thin-screen TV and in 27.0%, only tube television.
Of the 68.1 million households with television, 79.8% had converter (integrated or adapted) to receive the digital signal of open television, although they were not catching it. In 2016, this rate was 71.5%. In households with television, the percentage of those who had this device with a converter that already received the digital signal from open television grew from 57.3% (2016) to 66.6% (2017).
From 2016 to 2017, the share of households that did not have any of the three conditions of access to the digital television signal (converter, satellite dish or pay-tv service) fell from 10.3% (6.9 million) to 6.2% (4.2 million). In urban areas, the decrease was from 10.5% (6.1 million) to 6.1% (3.6 million), and in rural areas, from 9.0% (794 thousand) to 6.8% (598 thousand). Among the Major Regions, the highest percentages were in the North (11.3%) and in the Northeast (8.1%), both in urban and rural areas.
The percentage of households with television that had received the signal through satellite dish increased from 34.8% to 32.5%, in the rural area, it fell from 73.1% to 70.5% and in the urban area, from 29.0% to 26, 9%.
Pay-tv service was used in 32.8% of households with television in 2017 and 33.7% in 2016. In urban areas, this percentage ranged from 36.9% (2016) to 35.6% ( 2017) and, in rural areas, rose from 11.7% (2016) to 14.1% (2017).
Among households without pay-tv, 55.3% did not buy it because they considered it expensive and 39.8%, because there was no interest in the service, while only 1.6% did not buy it because it was not available in the area.

