2016 Continuous PNAD: 90.6% of the women and 74.1% of the men do household tasks or take care of persons
December 07, 2017 10h00 AM | Last Updated: December 11, 2017 03h22 PM
In 2016, 10.5 million (6.3%) of the 166,7 million persons aged 14 and over in the country performed some kind of activity for own consumption; 44.9 million (26.9%) took care of persons; 135.5 million (81.3%) did household tasks and 6.5 million (3.9%) did volunteer work.
Among persons who worked in the production of goods for the exclusive use of residents of the housing unit or or non-resident relatives, 77.6% worked with planting, fishing hunting and raising of animals. The second most common activity was production of coal, collection of firewood, straw or related material (17.3%), followed by manufacture of footwear, clothes, furniture, ceramic items, food or other products (11.6%) and construction of buildings, rooms, wells or other construction works (7.0%).
In 2016, 32.4% of the women at working age performed activities related to the care of residents of the housing unit or of non-resident relatives. Among men that proportion was 21.0%. By age, 43.8% of the women between 25 and 49 had performed that type of activity, whereas only 29.6% of the men in the same ge group had. Among men aged 14 to 24, the rate of care-related activities was 15.1%; among women, 29.5%.
In 2016, 81.3% of the population (135.5 million persons) aged 14 and over had done household tasks in their own housing unit or in that of a relative. Whereas 89.8% of the women had performed those activities, the male proportion was 71.9%.
In Brazil, 6.5 million persons did volunteer work in 2016, corresponding to 3.9% of the population aged 14 and over. The North (5.6%) and South (5.0%) Region had the highest rates of volunteer work, whereas the Northeast (3.0%), the lowest.
From the 6.5 million persons who did volunteer work, 6.0 million (91.5%) did it by means of an enterprise, organization, or institution. Regarding employment status, 4.2% of the employed persons did volunteer work, against 3.6% of the non-employed ones.
These are some highlights in the 2016 Continuous PNAD module "Other forms of work", which investigated persons aged 14 and over who performed at least one of the aforementioned activities for at least one hour, in the week of reference. Click here for further information.
Men aged 50 and over are the majority in production for own consumption
Among the 10.5 million persons who performed some activity for own consumption, men were the majority (51.9% or 5.5 million persons) in relation to women. The older the age bracket, the bigger the occurrence of this type of work.
In the analysis by color or race, it was observed that the highest rates of production for own consumption occurred among blacks and browns: 8.3% of brown men, 6.7% of black men, and 5.4% of white men had performed activities of that kind; among women, the rates were, respectively, 6.8%, 6.5% and 4.7%.
In the North and Northeast Region, the rates for black and brown persons reached a level of 10%, whereas, among White persons, that figure was around 7%. The Southeast and Central West recorded rates below 5%, regardless of the color or race reported. In the South Region, white and brown persons had similar rates, reaching about 8% in 2016, and above that observed among black persons (5.9%).
In 2016, 48.8% of the persons who conducted those activities were employed in the labor Market, with a proportion of 61.7% among men, and 35.0%, among women. The percentage of employed persons performing activities for own consumption was above 50% in the North (59.6%), South (57.3%) and Central West (52.9%).
Women are the majority regarding care of persons
In the comparison by sex, the rate of activities related to the care of persons performed by women (86.9%) surpassed that of men (65.0%), as well as the rate of aid to educational activities (71.7% for women and 58.8% for men). Other activities have more similar percentages, though always higher in the case of women.
Considering status in the housing unit, the rate of care of persons by women was highest in terms of spouses (39.0%), followed by heads of household (30.6%) and by daughters of stepdaughters (25.9%). Among men, the rate of performance both for heads of household or spouses was about 25%, whereas for children and stepchildren, 12.7%.
Among those who took care of residents, almost half was in charge of residents aged 0 to 5 years of age (49.6%) and 6 to 14 (481%). That is a sign of the importance of child care in the household. The cafe of the elderly (aged 60 and over) corresponded to 9.0% of the cases.
Percentage of persons aged 14 and over,
who took care of residents, by type of care, by sex – Brazil - 2016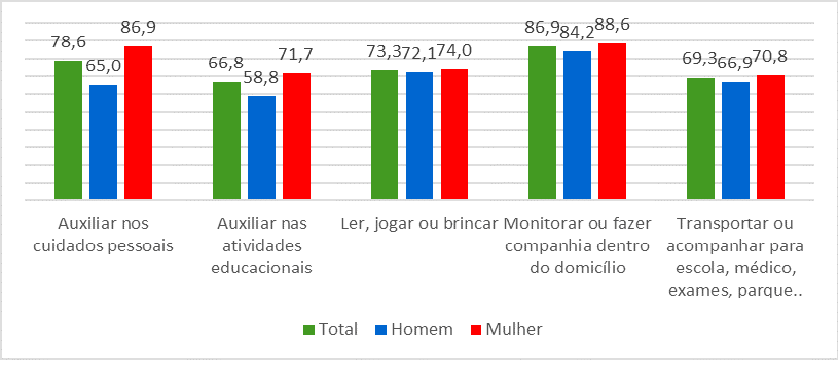
Source: IBGE, Diretoria de Pesquisas, Coordenação de Trabalho e Rendimento, Pesquisa Nacional por Amostra de Domicílios Contínua – 2016
Women spend twice as much time in care and other tasks
Continuous PNAD counted the number of hours dedicated to the care of persons and household tasks together, in order to calculate the intensity and difference in terms of male and female action. In 2016, the average number of hours spent per week in Brazil was 16.7 hours, with great discrepancy between the figures: 11.1 hours for men and 20.9 hours, on the average, for women.
The intensity of hours dedicated to those activities was higher among the unemployed: whereas the employed persons spent, on the average, 14.1 hours per week to those activities, the unemployed dedicated, on the average, 19.9 hours.
The rate of occurrence of domestic tasks by status in the household shows that, among women, spouses had the highest results, as follows: 95.6% of the spouses, 93.0% of heads of household and 80.7% of daughtrs or stepdaughters did household tasks. On the other hand, 80.6% of the male heads of household, 76.4% of the spouses and 57.6% of the children or stepchildren did those type of activity in 2016.
Regarding the type of activity conducted in the housing unit, women had a bigger percentage of participation in almost all the tasks listed, except “doing small repair ou maintenance in the housing unit, car, or household appliances, etc.”, task done by 65.0% of the men who did household tasks (versus 33.9% of the women). It is worth mentioning the big difference in the conduction of tasks “preparing or serving food, setting the table or washing the dishes” and “cleaning and maintenancr of clothes or footwear” among women and men: 95.7% versus 58.5% and 90,8% versus 55.7%, respectively).
In all the categories of color or race, women did more household tasks and provided care of persons than men
The rates that indicate the performing of domestic tasks by women surpassed those of men in the three groups of color or race: the rates of women were about 90%, and those of men were below the 74%, as shown in the graph below.
Rate of domestic tasks in the housing unit or in the housing unit of a relative, by color or race and sex - Brazil - 2016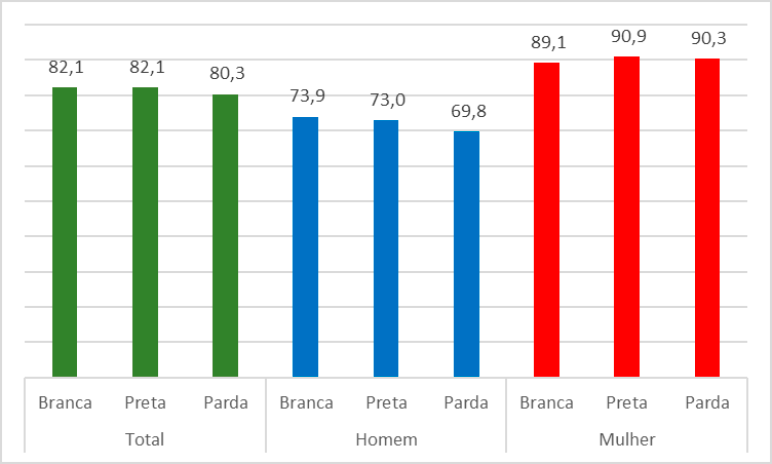
Source: IBGE, Diretoria de Pesquisas, Coordenação de Trabalho e Rendimento, Pesquisa Nacional por Amostra de Domicílios Contínua – 2016
The difference between the rates of domestic work of the three categories of color or race among women was less significant: 89.1% of the white women performed those activities, below the 90.9% of the black women and 90.3% of the brown ones.
As for the care of residents, the difference was bigger: 35.3% of the brown women and 34.0% of the black women took care of residents of the housing unit or or non-resident relatives, whereas among white women that rate was 29.3%.
Among men, the difference by color or race in this activity had lower intensity: 22.0% for blacks; 21.1% for browns and 20.7% for whites, in 2016. The North Region had the biggest percentage of persons taking care of residents or of non-resident relatives (31.4%) and the Southeast, the lowest (25.7%).
Women are also the majority in volunteer work
The rate of volunteer work was higher among women (4.6% than among men (3.1%) in Braziland in the Major Regioms. In terms of number of hours dedicated to those activities, however, there is not much difference: men spent, on the average, 6.9 weekly hours in volunteer work, and women, 6.6 hours.
The rate of volunteer work increases with age: 2.5% for persons aged 14 to 24, 4.1% for persons aged 25 to 49 anos and 4.6% for those aged 50 and over.
The survey investigated the place where volunteer work was done, with the possibility of more than one answer, in this case. Most people did volunteer work in religious congregations, unions, compounds, political parties, schools, hospitals, retirement homes. In Brazil this category represented 81.5% of the persons who did volunteer work, with the biggest percentage recorded by the North Region, and the smallest, by the South (74.9%).
In the South Region, 20.2% of the persons aged 14 and over did volunteer work in another pace, including the services provided to residents of a community or locality, conservation of the environment or animal protection and third parties doing housework or providing care by means of free professional services.

