Summary of Social Indicators
IBGE shows that one out of every four older adults were employed in 2024
December 03, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: December 10, 2025 05h00 PM
Highlights
- Approximately 1 out of every 4 older adults was employed in 2024.
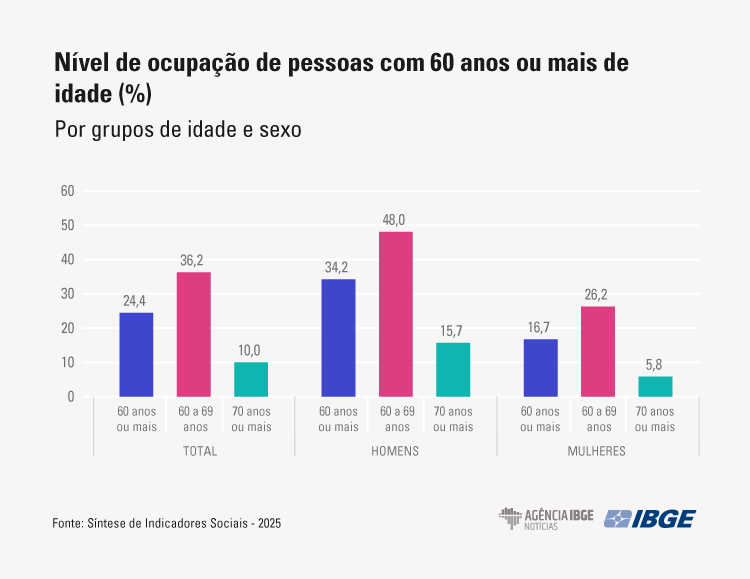
- At the age of 70 years and over, 15.7% of men and 5.8% of women remain employed.
- Average usual real earnings of persons aged 60 years and over (R$ 3,108) was 14.6% above that of persons aged 14 years and over.
- Unemployment rate (6.6%) was the lowest in the series initiated in 2012, but employed persons without a formal contract increased participation, having reached 46.5% in 2024.
- The total employed population reached the highest level in the annual series, with about 101.3 million persons in the year.
- The employment population ratio of women with a higher education degree (75.9%) was 3 times higher than that of women without schooling or with incomplete primary school (25.3%).
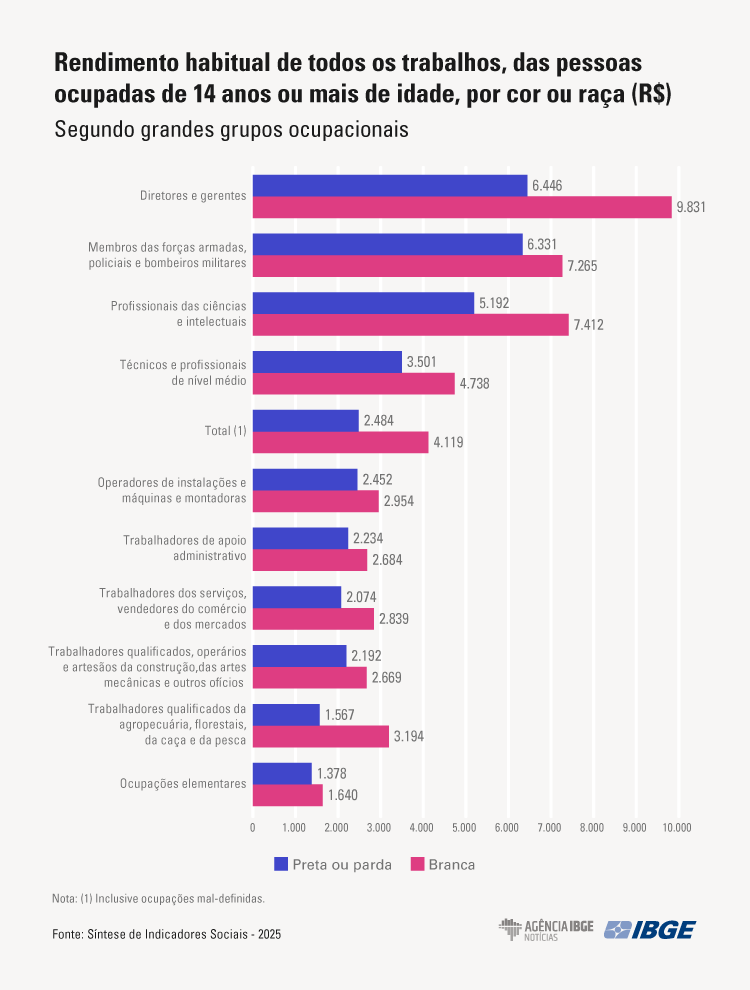
- Income of the white population is about 65% higher than that of the black and brown population.
- Maranhão (R$ 2,051) and Ceará (R$ 2,053) were the Federation Units with the lowest average income. The highest were found in the Federal District (R$ 5,037) and São Paulo (R$ 3,884).

The population aged 60 and over increased from 22 million to 34.1 million, between 2012 and 2024, a percentage increase of 53.3%. The employment population ratio of this group was 24.4%, being 34.2% among men and 16.7% among women. That is, approximately 1 out of every 4 older adults were employed in 2024.
Underutilization rates (13.2%) and unemployment rates (2.9%) were significantly below those of the average population, 16.2% and 6.6%. Information comes from the chapter on Economic structure and labor market in one of the main IBGE studies, Summary of Social Indicators: An analysis of the Brazilian population's living conditions 2025. The study has other two chapters: Education and Standard of living and income distribution.
In 2024, between 60 and 69 years of age, almost half of men (48.0%) and slightly more than one fourth of women (26.2%) were employed. At the age of 70 and over, 15.7% of men and 5.8% of women still remained employed in the labor market.
"The rise of life expectancy and the changes observed in family arrangements in the last few years, together with labor market informality in Brazil and the reform in the Social Security System are factors that tend to keep people in the labor market longer," Denise Freire, analyst of the study, explained.
In 2012, the employment population rate of older adults aged 60 and over was 22.0%, reaching 23.1% in 2019, but dropping to 19.8% (2020) and 19.9% (2021) during the Covid-19 pandemic years. Recovery of around two percentage points per year occurred in 2022 (21.3%) and 2023 (23.0%), reaching 24.4% in 2024.
According to Denise Freire, throughout the time series of the survey, it can be seen that the percentage of seniors in the labor market has grown. "Then the pandemic happened, and there was a significant drop in the employment rate because this group really needed to protect themselves. But, after the most critical period of the pandemic, this group has been resuming its participation in the labor market, reaching the highest percentage in 2024," she explained.
The inclusion of older adults people in the labor market by occupation occurs mainly through self-employment (43.3%) and as an employer (7.8%), compared to people aged 14 or older in the labor market, who had 25.2% and 4.3% in these positions, respectively.
The average usual real income from the main job for persons aged 60 and over (R$ 3,108) was 14.6% higher than that of persons aged 14 or older. Older women earned R$ 2,718, an amount 33.2% lower than what men earned, R$ 4,071, and Black or mixed-race perons earned R$ 2,403, 48.7% less than white persons, R$ 4,687. While in the 14 to 29 age group, the hourly wage was R$ 13.30, for persons aged 60 and over it was almost twice as much, R$ 25.60.
Unemployment rate of 6.6% in 2024 is the lowest in the time series that started in 2012
In 2024, the unemployment rate (6.6%) was the lowest in the time series that started in 2012, below the rate recorded in 2014 (7.0%). The employment population rate reached the peak in the series (58.6%), with men reaching 68.8% against 49.1% for women.
However, workers without a formal contract increased their share from 2021, reaching 46.5% in 2024, while the employed population with a formal contract was 47.9%. Among workers without a formal contract, the growth rate was higher for those without a contract (4.2%) than for self-employed workers (1.8%).
In absolute figures, the total increase of employed persons in 2024 from 2023, reached 2.6 million persons. The employed population reached the highest level in the current series, with approximately 101.3 million persons a year.
The employment population ratio of women with a higher education degree (75.9%) was 3.0 times higher than that of women with no education or incomplete primary education (25.3%). Among men, the employment rate of those with a higher education degree (86.0%) was 1.6 times higher than that of men with no education or incomplete primary education (52.6%).
Youngsters (ages 14 to 29), who accounted for about one-third of employed individuals in 2012, saw their share decrease each year, with the lowest point in 2020 (25.8%) due to the COVID-19 pandemic. In the following years, there was a slow recovery, reaching 26.5% of employed individuals in the labor market by 2024.
In turn, people aged 50 to 59 and older adults (60 years or older) increased their participation between 2012 and 2024. In 2012, these two groups combined accounted for 19.1% of employed persons, and in 2024, 24.3%. The participation of the intermediate age group, from 30 to 49 years, showed a trend to increase until 2020 (51.3%), later starting a declining path until 2024, when it reached 49.2%, a level close to that observed in 2015.
Income of the white population is about 65% higher than that of black and brown populations
In 2024, the employed white population earned, on average, 65.9% more than the black or brown population, and men earned 27.2% more than women, considering income from all jobs. The real average hourly wage was R$24.60 for white persons, while black and brown persons earned R$15.00.
"In 2024, an increase in the average real income from all jobs was recorded, however, inequalities by color and race and by sex remain. There are high inequalities, with the male population receiving more than the female population and the white population more than blacks and browns. Compared to the beginning of the series, there is a reduction in the level of inequality, but it still remains at significant levels," said the study's analyst, João Hallak.
The average usual real earnings of the employed population in the main job changed from R$3,002 per month in 2023 to R$3,108 in 2024, an increase of 3.5%, accumulating a rise of 10.8% in real terms in the 2023-2024 biennium. The three groups with the highest usual income from all jobs in 2024 were "Directors and managers" (R$8,721), "Members of the armed forces, police and military firefighters" (R$6,749) and Science and intellectual professionals" (R$6,558).
Domestic services (R$ 1,241) had earnings below 40% of the total average income. Meanwhile, the sectors of Information, financial and other professional activities (R$ 4,442) and Public administration, education, health and social services (R$ 4,412) recorded the highest figures, considerably above the overall average.
In 2024, considering the average income from all jobs, persons employed in the North (R$ 2,450) and Northeast (R$ 2,229) regions received, respectively, 76.4% and 69.5% of the national average. Maranhão (R$ 2,051) and Ceará (R$ 2,053) were the states with the lowest average monthly income. The highest were in the Federal District (R$ 5,037) and São Paulo (R$ 3,884).
More about the survey
The Summary of Social Indicators: an analysis of the Brazilian population's living conditions 2025 aims to systematize and present a set of information related to the social reality of the country, based on highly relevant structural themes. In this edition, the topics are organized into three fundamental and complementary axes: Economic structure and labor market; Standard of living and income distribution; and Education. Additionally, in this edition, groups of occupation, the profile of older adults in the labor market, and a study on poor workers, also known as the Working Poor, are addressed.




















