Continuous PNAD
For the first time, more than half of the population accesses the Internet from a TV
July 24, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: July 26, 2025 10h16 PM
Highlights
- In 2024, among the 188.5 million persons aged 10 and over in the country, 89.1% (or 168.0 million) have used the Internet in the last three months, being 90.2% in the urban area and 81.0% in the rural area.
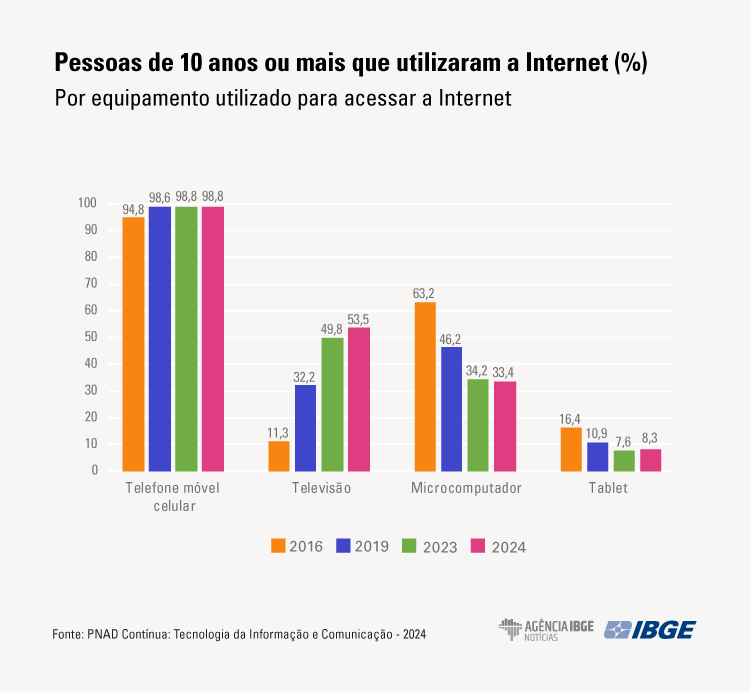
- The percentage of persons who accessed the Internet from a personal computer fell from 63.2%, in 2016, to 33.4%, in 2024. The percentage of access to the Internet from a TV went from 11.3% in 2016, to 53.5%, in 2024, surpassing, for the first time, more than Half of Internet users.
- In 2024, the percentage of White persons who used the Internet in the period of reference amounted to 90.0%, slightly above that of black persons (88.4%) and brown persons (88.6%). In 2016, inequality was even higher: 72.6% of the White persons, 63.9% of the black persons and 60.3% of the brown ones had used the Internet.
- From 2019 to 2024, the proportion of elderly persons using the Internet increased from 44.8% to 69.8%, the highest among the age groups analyzed.
- In 2024, among the persons who used the Internet in the period of reference, 10.5% accessed the service for free, in public establishments (schools, universities or libraries).
- From 2022 to 2024, the purposes of Internet access with the greatest increases were: access to banks and financial institutions (from 60.1% to 71.2% of the users), buying or ordering goods and services (from 42.0% to 48.1%) and using some type of public service (from 33.4% to 38.8%).

In 2024, of the 188.5 million persons aged 10 and over in Brazil, 89.1% (or 168.0 million) have used the Internet in the period of reference iin the last three months. The main means for access reported was, notably, the mobile telephone (98.8%), followed by the television (53.5%), the personal computer (33.4%) and the tablet (8.3%). These data come from the annual Continuous PNAD module on Information and Communication Technology (TIC), released today (24) by the IBGE. Read also the news on information and communication technology in housing units and on the ownership of a mobile telephone for personal use.
Between 2023 and 2024, there was an increase in persons using a television or tablet to access the Internet (3.7 p.p. and 0,7 p.p., respectively) and a reduction in the use of the personal computer (-0.8 p.p.).
The access to the Internet from a personal computer fell from 63.2%, in 2016, to 46.2%, in 2019, and hit 33.4% in 2024, olowest figure in the time series. However, among higher education or graduate students, more than ¾ acessed the Internet from a personal computer in both educational systems: 77.4% in the public system and 77.5% in the private one.
The percentage of persons accessing the Internet from a television increased from 11.3%, in 2016, to 32.2%, in 2019, until it reached half of the users in 2024 (53.5%). The use of tablet, n turn, had a trend to decrease between 2016 and 2022, but remained stable in 2023, and recorded a slight positive change in 2024.
Gustavo Fontes, analyst of the survey, explains that “in the period covered by the survey, we have observed important changes in the use of equipment to access the Internet. There was a significant increase in the use of the television for this prurpose, surpassing, in 2024, more than half of the Internet users, which can reflect, among other factors, the advance of streaming platforms. On the other hand, the use of a computer to access the Internet has been on a downward trend since the start of the series, in spite of the deceleration observed since 2023. Among students, in 2024, there was an interruption of the decrease in the use of computers to access the Internet.”
In 2024, whereas 72.9% of the students in the private education system accessed the Internet from a personal computer, this percentage was only 29.2% among those in the public system. the percentage of use of a television set to access the INternet reached 72.6% among students in the private system, also higher than the figure for students in the public education system (53.2%).
The mobile telephone was the main type of equipment used to access the Internet by students both in the public (97.2%) and in the private education system (98.6%).
Use of the Internet in a rural area changes from 33.9% in 2016 to 81.0% in 2024
In 2016, starting year of the series, 66.1% of the population aged 10 and over had used the Internet in the period of reference, with an increase to 89.1% in 2024. In 2023, 88.0% of the persons aged 10 anos had used the Internet. Although Internet use is lower among residents of rural areas, there was a significant increase of its use in thi population group, from 33.9% in 2016 to 81.0% in 2024. In the same period, percentages of Internet use in urban areas went from 71.4% to 90.2%.
In 2024, the Central West Region (93.1%) concentrated the biggest proportion of persons who sued the Internet, whereas the North (88.2%) and Northeast (87.2%) kept the lowest results. Nevertheless, these two Major Regions had the biggest expansion of this indicator from the preceding year, with increases of 2.9 p.p. and 3.0 p.p., respectively; in the Southeast, the proportion of persons recorded a negative change of 0.6 p.p last year. In the period 2019 - 2024, the north and Northeast recorded increases of 18.2 p.p. and 17.2 p.p. in this indicator, respectively, showing that regional inequality regarding Internet access has decreased.
Inequality of access to the Internet by color or race decreases
Inequality of access to the Internet by color or race has been reduced throughout the series. In 2024, the percentage of white persons who used the Internet was 90.0%, a little more than estimated for black persons (88.4%) and brown persons (88.6%). In 2016, differences were more pronounced: 72.6% of white persons, 63.9% of black persons and 60.3% of brown persons had used the Internet.
As for the sex, 89.8% of the women used the Internet in 2024, a slightly above the percentage of men (88.4%). By level of education, persons with no schooling (46.0%) had a percentage of Internet use significantly below that of other schooling groups, mainly persons with incomplete higher education (97.9%) and a higher education degree (97.2%).
Use of the Internet among the elderly shows the biggest increase
In 2024, the percentage of persons using the Internet in the period of reference, in the group aged 10 to 13 was 84.8%. This percentage increased successively in the subsequent age groups and reached 96.4% among persons aged 25-29. The proportion of users then fell to 89.9%, among persons aged 50 - 59, and to 69.8% among older adults over 60.
The increase in the percentage of persons using the Internet between 2019 and 2024 was very significant in the group aged 60 and over: from 44.8% to 69.8% (an increase of 25.0 p.p.), followed by persons aged 50 - 59: from 74.4% to 89.9% (an increase of 15.5 p.p.). From 2023, these groups also had the biggest increases in the percentage of Internet users (3.8 p.p. and 1.9 p.p., respectively).
92.4% of the students accessed the Internet in 2024
In 2024, the percentage of persons using the Internet were 92.4%, among students, and 88.4%, among non-students. Against the previous year, there was an increase of Internet use among non-students (1.3 p.p.) whereas among students the increase hit 0.5 p.p.
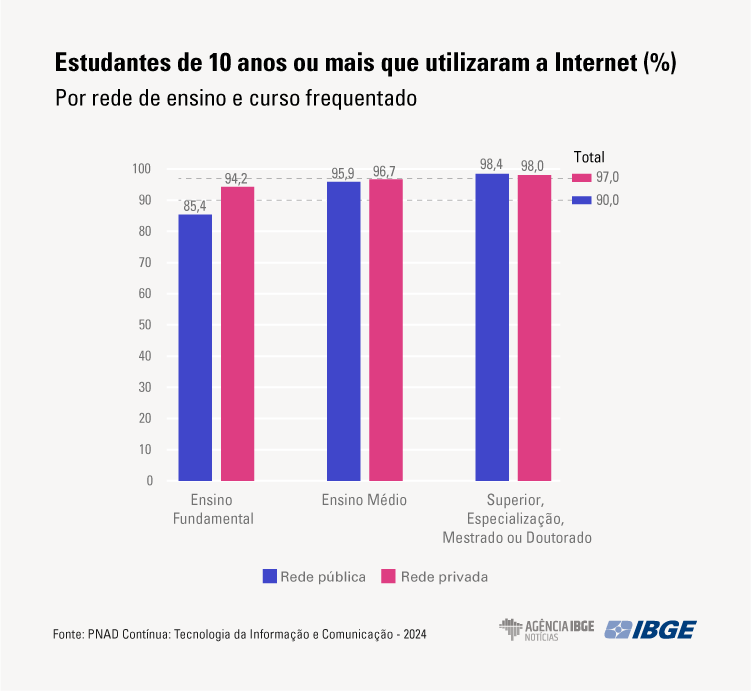
While 97.0% of the students in the private education system used the Internet in 2024, the percentage among students in the public system was 90.0%.
Among students in primary school, 94.2% in the private system and 85.4% in the public system used the Internet (a difference of 8.8 p.p.). However, among high school students, the percentages were, respectively, 95.9% and 96.7%, a difference of only 0.8 p.p. Among those who were in high school or in graduate courses (specialization, master's or doctoral courses) the proportions of access were closer to total in both education systems (98.0% of the students in the private system and 98.4% of those in the public system used the Internet).
Proportion of daily access to the Internet reaches 95.2% in 2024
In 2024, among persons aged 10 and over who used the Internet in the period of reference of the last three months, 95.2% used the Internet regularly every day; 1.9% used it almost every day (five or six days a week); 2.4%, one to four times a week; and only 0.6% used it less than once a week.
Continuous PNAD started to investigate, in 2022, people's frequency of access to the Internet. the percentage of persons using the Internet daily, on a regular basis, went from 93.4%, in 2022, to 94.3%, in 2023, and to 95.2%, in 2024.
Access to banks recorded the biggest increase among reasons for using the Internet from 2022 to 2024
Acccessing the Internet to make voice or video calls remained as the most often reported reason, by 95.0% of the users in 2024. This proportion changed positively by 0.4 p.p. from 2023 (94.6%) and increased 3.6 p.p from 2019 (91.4%). Tghhe second most indicated reason was sending or receiving text messages, voice messages or imagesby different e-mail apps (90.2%). This use fell by 0.9 p.p. from 2023 (91.1%) and also dropped 5.6 p.p. from 2019 (95.8%).
Outras finalidades apontadas por mais da metade dos usuários da Internet foram: assistir a vídeos, inclusive programas, séries e filmes (88,5%); usar redes sociais (84,2%); ouvir músicas, rádio ou podcast (83,5%); acessar bancos ou outras instituições financeiras (71,2%); ler jornais, notícias, livros ou revistas pela Internet (68,9%); e enviar ou receber e-mails (60,8%).
Other activities carried out on the Internet and included in the survey covered less than half of the users: buying or ordereing services (48.1%); using some kind of public services (38.8%); playing (30.2%); and selling or advertising goods or services (12.3%).
From 2022 to 2024, the reasons for accessing the Internet that increased the most were: accessto banks and financial institutions (from 60.1% to 71.2% of the users), buying or ordering goods and services (from 42.0% to 48.1%) and using some type of public service (from 33.4% to 38.8%). Gustavo Fontes observes: “Som purposes for Internet use recorded a significant increase from 2022 to 2024, for example, accessing banks and other financial institutions, for example. In only two years, there was an increase of 22 million persons in the group that used the Internet to access banks. Other purposes on an upward trend were buying or ordering goods or services (almost 13 million persons more) and using some type of public service (increase by more than 11 million persons)”.
In 2024, 10.5% of the users accessed the Internet for free from public places
In 2024, 10.5% dof the persons who used the Internet in the period of reference of the last three months said they accessed the service for free from public education establishments (such as schools and universities) and public libraries (8.9% in 2022 and 10.2% in 2023).
The proportion of students who used free access to the Internet from public education establishments and public libraries was 29.6% in 2024, 2.5 p.p. above the figure in 2023 (27.1%). Among students in the public system, a little more than 1/3 (34.3%) of those who used the Internet in the period of reference accessed the service for free in schools, universities or public libraries. In 2023, this percentage was 30.5%.
The analysis by course attended, among students in the public system who used the Internet, 27.4% of the students in primary school, 39.3% of those in high school and 52.3% of those in higher education or graduate courses accessed the Internet for free from schools, universities or public libraries in 2024. There was an increase in all groups from 2023, whose percentage were, respectively, 25.3%, 33.9% and 45.5%.
In the country, 30.9% of the students in the public system (regardless of having accessed the Internet in the period of reference) accessed the Internet from schools, universities or public libraries last year, which represents an increase of 3.6 p.p. from 2023, when the percentage was 27.2%. In 2022, first year of the time series for this indicator, the percentage was 23.9%.
Privacy and security are among the main reasons for children not to use the Internet
In 2024, 10.9% of the persons aged 10 and over (or 20.5 million persons) did not use the Internet in the period of reference, against 12.0% in 2023 and 20.5% in 2019. The two main reasons for not accessing the Internet were not knowing how to use it (45.6%) and lack of necessity (28.5%). The reasons that followed were e conomy-related (expensive Internet access services, and expensive necessary equipment) and amounted to 10.9%. Lack of time was mentioned by 4.3% of persons and concern with privacy or security, by 3.8%.
Among those who did not access the internet in 2024, 73.4% had no schooling or had incomplete primary school and 52.1% were aged 60 and over.
For the population aged 60 and over, the main reasons were not knowing how to use the Internet (66.1%), and lack of necessity (22.1%). Children aged 10 to 13 were 8.6% of those who did not use the Internet, the second most numerous age subdivision, and their main reasons were lack of necessity (33.9%) and concer with privacy or security (22.5%). This second reason seems to evidence fear by parents or caregivers. Economic reasons stand out in this younger group: necessary economic equipment was expensive (9.3%) and Internet access services were expensive (8.9%).
Gustavo highlights that “in the period 2022 - 2024 it was observed that, among younger persons and students that did not use the Internet, the share of persons reporting concern with privacy or security as the main reason for not accessing the Internet increased, year after year, which tends to reflect, mainly in the case of children and teenagers, a concern of parents or caregiverss. Financial motivations have reduced participation.”
More about the survey
Since 2016, the annual module on Information and Communication Technology (ICT) of the Continuous National Household Sample Survey (Continuous PNAD) analyses the access to the Internet and the ownership of a mobile telephone for personsl use, disaggregated by geographies: Brazil and Federation Unnits. Access the support material and see the complete publication for additional information.




















