2022 Census
2022 Census: Brazil has 11.8 million residents in Conservation Units
July 11, 2025 10h00 AM | Last Updated: July 17, 2025 11h55 AM
Highlights
- The 2022 Population Census shows that 11,809,398 people live in Conservation Units (CUs), a number that represents 5.82% of the Brazilian total population.
- The population that identifies itself as brown comprises most residents in CUs, representing a total of 6,037,270 people (51.12%), followed by white persons, with 4,229,681 people (35.82%) and black persons, with 1,407,255 (11.92%).
- Regarding traditional peoples and communities, quilombolas represent 2.39% of the resident population in CUs, with a total of 282,258 people, and indigenous people are 1.12%, or 132,804 people.
- Nearly all the persons (98.73%) who live in CUs are in areas of sustainable use, such as environmental protection areas and extractive reserves.
- Environmental protection areas concentrate 97.10% of the resident population in CUs.
- The Integral Protection management group houses 131,492 people, which corresponds to 1.11% of the resident population in Conservation Units. The highest number is found in Maranhão, with 38,176 (29.03%) people in Integral Protection CUs, followed by Rio de Janeiro, with 30,633 (23.30%) and São Paulo, with 9,954 (7.57%).
- The survey also identified 1,138 (48.11%) CUs with resident people and 1,227 (51.88%) without inhabitants.
- Four out of ten residents (40.34%) in CUs live in housing units with at least one category of precarity or absence of basic sanitation, such as absence of water supply, garbage destination and sewage disposal.
- On the other hand, 856,495 people, or 7.31% of the population in CUs, deal with simultaneous precarities of water supply, garbage destination and sewage disposal. This proportion is higher when compared with the total Brazilian population.
- Concerning households with at least one indigenous resident in CUs, 59.94% (29,482) lived with some sort of precarity, adding up to 94,051 indigenous persons. Concerning households with at least one quilombola resident in CUs, the proportion is higher, with 85.94% (82,457) living with some sort of precarity, the equivalent to 248,064 quilombola persons.
- In the CUs, 46,239 (1.16%) housing units had no bathroom or toilet. In Integral Protection units, 1,985 (4.87%) housing units were in this condition. In the full set of permanent private housing units in Brazil, the percentage of housing units in this situation (0.59%) is lower.

The 2022 Population Census shows that 11,809,398 people live in Conservation Units (CUs) in Brazil, a figure that represents 5.82% of the entire Brazilian population. Almost all the people (98.73%) who live in CUs area in areas of sustainable use, which corresponds to 11,658,936 residents. The survey pinpointed 1,138 (48.11%) CUs with residents and other 1,227 (51.88%) uninhabited. Established by law, the CUs are territories with relevant natural characteristics for the conservation of the Brazilian biological diversity, which can be of sustainable use, like areas of environmental protection and extractive reserves, and of integral protection, like biological reserves and stations.
Never published information is part of the publication 2022 Population Census: Conservation Units - Main characteristics of residents and households by geography and specific population group - Population results, which brings the main characteristics of residents and households in these localities, including indigenous and quilombola persons. To produce the publication, the IBGE used official data from the National Register of Conservation Units on the reference date of the survey, maintained by the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change with the collaboration of managing offices at the federal, state and municipal levels.
The event presenting the results will be held at 10 am (Brasília standard time) at the Garibaldi Brasil Amphitheater, in the campus of the Federal University of Acre (UFC), in Rio Branco (AC), with live broadcast on Digital IBGE and the IBGE´s social media. The results can be accessed on the IBGE portal and on platforms like SIDRA, Census Overview and the Interactive Geographic Platform (PGI), and they can be viewed through interactive maps in the last two ones.
Precarities in sanitation affect four out of ten CU residents
Four out of ten residents (40.34%) in CUs live in housing units with at least one category of precarity or absence of basic sanitation, like water supply, sewage disposal and garbage destination. That proportion is higher in the population in CUs than the entire Brazilian population. In absolute figures, 4,725,613 people are affected by this situation in the CUs. Concerning households with at least one indigenous resident in CUs, 59.94% (29,482) lived with some sort of precarity, adding up to 94,051 indigenous persons. Concerning households with at least one quilombola resident in CUs, the proportion is higher, with 85.94% (82,457) living with some sort of precarity, the equivalent to 248,064 quilombola persons.
On the other hand, 856,495 people, or 7.31% of the population in CUs, deal with simultaneous precarities of water supply, garbage destination and sewage disposal. That proportion is higher when compared with the entire Brazilian population, which has 3.00% of the people in this most serious precarious situation.
"The access to an appropriate basic sanitation is a key element of life and environmental quality. We find higher percentages of inadequacy of sanitation in housing units within CUs, which can result in greater risks of contamination and environmental degradation, precisely in areas created with the purpose of guaranteeing the right to the balanced environment, ”explains Fernando Damasco, IBGE´s Manager of Traditional Territories and Protected Areas.
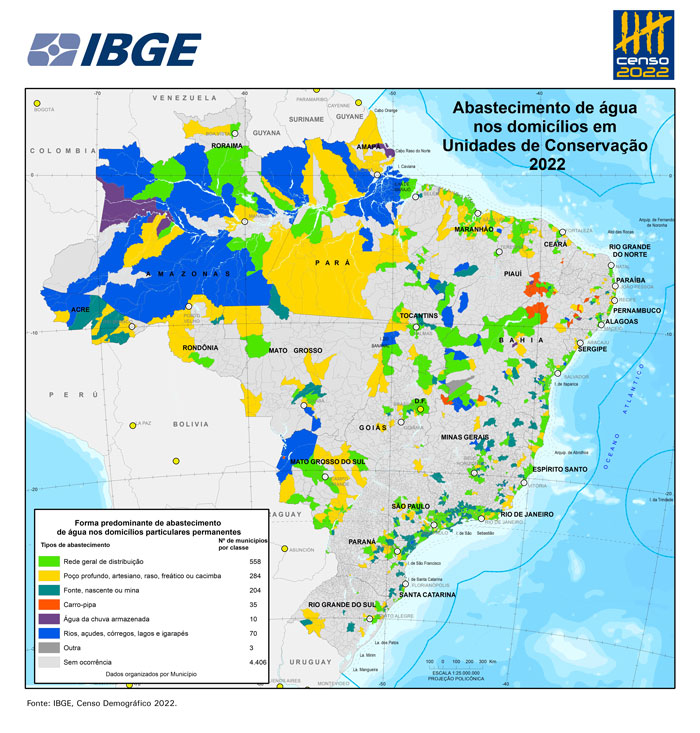
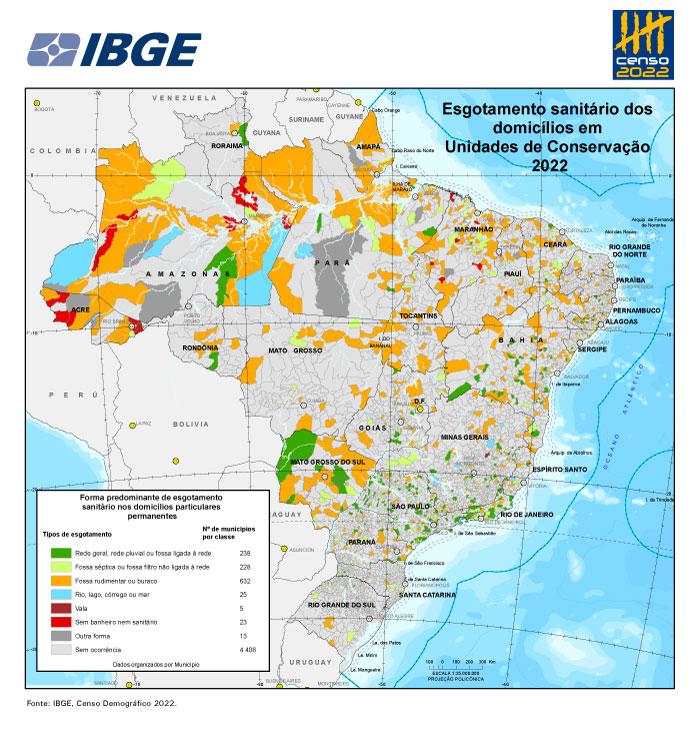
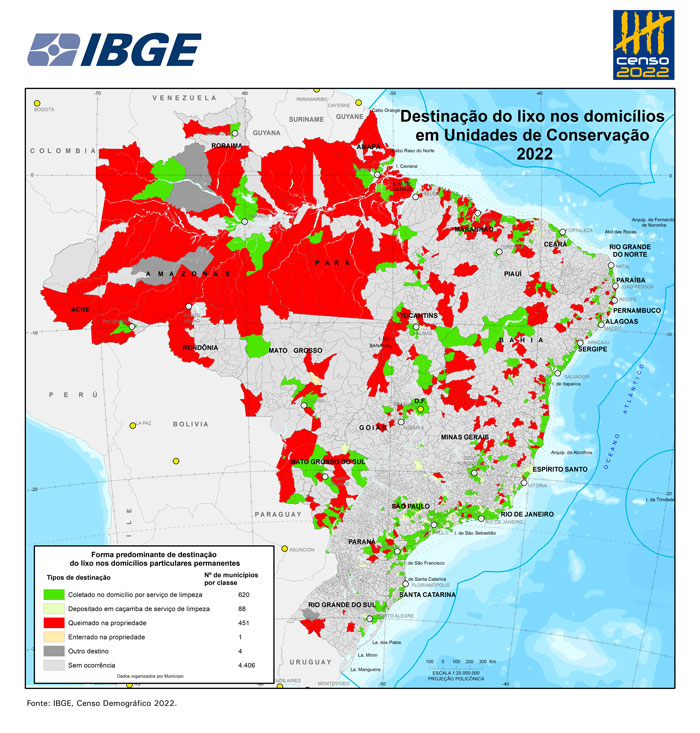
In the CUs, a total of 46,239 (1.16%) housing units had no bathroom or sanitary, in which 158,594 (1.35%) people were living. In Integral Protection units, 1,985 (4.87%) housing units were in this condition, housing 8,968 (7.20%) people. In the full set of permanent private housing units in Brazil, the percentage of housing units in this situation (0.59%) is lower.
The results of the 2022 Census also show that the illiteracy rate in CUs is 8.84%, above the national rate of 7.00%. Of the 9,245,172 people 15 years or older who live in CUS, 817,383 are illiterate. Regarding indigenous and quilombola persons 15 years or older, the literacy rate does not show significant differences concerning the location of their housing units in CUs or outside them.
The IBGE's Manager of Traditional Peoples and Communities, Marta Antunes, makes a remark about the educational results for these populations. "It should be noted that literacy rates of traditional peoples are lower.”
The composition of the resident population in the CUs by sex and age reveals the predominance of men in relation to women in the age ranges below 30 years and of women in the ranges over 30 years. The survey also shows that, in CUs, the population is younger than that found in the total resident population in Brazil. The North Region has a younger age structure and the South and Southeast regions, more aged structures.
In the categories of extractive reserves, sustainable development reserves and forests, it was identified that the age pyramid tends to a triangular format, very close to that verified for the whole indigenous population, indicating that these areas are home to younger populations than the whole population in CUs and the total resident population in Brazil.
Environmental Protection Areas concentrate 97.10% of the resident population in CUs
The most populous CU category is that of environmental protection areas, gathering 11,466,934 resident people (97.10% of the total people in CUs). They are followed by extractive reserves, which gather a population of 122,239 (1.04%).
Together, extractive reserves, sustainable development reserves and national, state or municipal forests, categories that provide for the presence of extractive populations, account for a 198,508 people (1.68%). The areas of ecological interest had 52,079 resident people (0.44%).
Among the integral protection units, the national, state or natural municipal parks had the largest population, with 117,325 people (0.99%), an amount that stands out among the other categories of the group. They are followed by wildlife refuges, with 16,978 (0.14%) people, natural monuments, with 8 474 (0.07%) people, biological reserves, with 6,123 (0.05%) and ecological stations with 3,136 (0.03%).
Private reserves of the natural heritage house 3,573 (0.03%) people.
|
People living in Conservation Units, |
|
|---|---|
| Ecological Station | 3,136 |
| Biological Reserve | 6,123 |
| Park | 117,325 |
| Natural Monument | 8,474 |
| Wildlife Refuge | 16,978 |
| Environmental Protection Area | 11,466,934 |
| Area of Relevant Ecological Interest | 52,079 |
| Forest | 33,507 |
| Extractive Reserve | 122,239 |
| Fauna Reserve | - |
| Sustainable Development Reserve | 42,762 |
| Private Natural Heritage Reserve | 3,573 |
Most residents identify themselves as brown persons in CUs
The population that identifies itself as brown comprises most residents in CUs, representing a total of 6,037,270 people (51.12%), followed by white persons, with 4,229,681 people (35.82%) and black persons, with 1,407,255 (11.92%). Regarding traditional peoples and communities, quilombolas represent 2.39% of the resident population in CUs, with a total of 282,258 people, and indigenous people are 1.12%, or 132,804 people.
“It is interesting to note that in the CUs we have higher percentages of black, brown, indigenous or quilombola people compared to the percentages of these groups in the Brazilian population. They are groups that historically play a relevant role in environmental conservation and appeared more prominently in the results of the study,” says Antunes.
The North stands out for the presence of brown persons living in CUs, who correspond to 71.68% of the resident population. The states of that region with the highest weight of the brown population living in CUs are Roraima (74.74%), Pará (73.80%) and Acre (72.58%). On the other hand, the Northeast Region has the highest relative weight of black persons (16.03%), being in Bahia the highest proportion (26.06%) of persons who declared black living in CUs. Amapá is the second state with the highest concentration of black population living in CUs (21.15%) and Sergipe, the third one, with 16.76%.
Most indigenous population in CUs live in rural situation
The 2022 Census also reveals that 7.84% (132,804 persons) of the indigenous population live in CUs. Concerning the distribution of that population, the Northeast gathers the largest amount of indigenous people living in CUs, with 49,111 persons, which corresponds to 9.28% of the indigenous population in the region. It was followed by the North Region, with 47,027 indigenous persons (6.24%). More than one quarter (25.71%) of the indigenous population living in CUs is in Amazonas, 34,143 people, whereas Bahia concentrates 29,908 indigenous persons in CUs. Those two states gather 48.23% of the indigenous population living in these areas.
When considering the entire country, the indigenous people live predominantly in urban situation (53.97%), though most of that population living in CUs live in rural situation. The 2022 Census data show that the Central-West stands out for the lowest proportion of indigenous population living in CUs in urban situation (27.16%), followed by the North (35.79%) and South (45.61%). Among the states, Amapá has 100% of the indigenous population living in CUs in rural situation. Acre and Roraima also have a significant proportion, with more than 90% of their indigenous population living in the same condition.
The North Region has the highest percentage of indigenous persons in the total number of persons living in CUs (4.89%), followed by the Northeast (1.11%). The state with the highest relative weight of indigenous population among those living in CUs is Paraíba (23.41%), followed by Amazonas (13.04%) and Mato Grosso do Sul (9.89%).
Whenever the distribution of the resident indigenous population by management group of CUs is compared with the total resident population by group, a higher relative weight of the indigenous population is noticed in areas of integral protection. In other words, of the indigenous persons living in CUs, 8.74% (11,603) are in areas of integral protection, against 1.11% of the total population. Amazonas stood out, with 5,408 indigenous persons in areas of integral protection, followed by Bahia, with 3,381 and São Paulo, with 613. Integral protection units aim at preserving nature, allowing only the indirect use of their natural resources, except for cases established by law.
The highest number of indigenous persons in integral protection units is found in the National Park of Pico da Neblina (AM), with 4,361 people, in the National Park of Monte Pascoal (BA), with 3,771 people and in the State Park of Serra do Aracá (AM), with 3,062.
Maranhão and Bahia concentrate 82.17% of the quilombola population living in CUs
Among the quilombola population, 21.22% (282,258) live in CUs. The Major Region with the highest number of quilombola persons living in CUs is the Northeast, with 243,066 people, which corresponds to 26.82% of the quilombola population living in the region. It is followed by the North, with 19,942 quilombola persons, which corresponds to 11.92% of the quilombola population living in the region.
Most of the quilombola population living in CUs is in Maranhão, with 60.44% (170,606 quilombola persons) of the quilombola persons living in CUs, whereas Bahia concentrates 21.73% (61,331 quilombola persons). Together, the two states account for 82.17% of the quilombola population living in CUs, whereas the Northeast concentrates 86.11% of the quilombola people in CUs.
The Northeast has the highest percentage of quilombola persons in the total number of persons living in CUs (5.52%), followed by the North (2.07%). The state with the highest relative weight of quilombola population among those living in CUs is Amapá (19.15%), followed by Maranhão (10.97%) and Bahia (4.53%).
In the case of the quilombola population living in CUs, 69.33% have their housing units in rural situation, a level slightly above that of the quilombola population in rural situation in Brazil (61.71%). The Central-West stands out for the highest proportion of quilombola persons living in CUs in urban situation (77.61%). Concerning the states, the highlights are Amazonas, Piauí, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul, with the entire quilombola population living in CUs in rural situation.
Northeast and Southeast concentrate 74% of those living in CUs
The Northeast is the Major Region with the largest population living in CUs, with 4,404,809 (8.06% of its resident population), followed by the Southeast, with 4,334,009 (5.11%). Together, the two regions concentrate 74% of the population living in CUs. On the other hand, the Central-West has the biggest relative share, with 9.95% of its population living in CUs.
Federal District and Maranhão were the Federation Units with the highest proportion of residents in UCs, with 39.16% and 22.96%, respectively. Those two Federation Units concentrate the most populous CUs as well. Among them, the Environmental Protection Area of the Central Plateau (DF), with 601,773 residents, followed by the Environmental Protection Area of the Baixada Maranhense (MA), with 583,882 people, and the Environmental Protection Area of UpaonAçu / Miritiba / Alto Preguiças (MA), with 509,977 people.
The states with the lowest relative weight of people living in CUs are Roraima, with 0.50% (3,211 people), Rondônia, with 0.65% (10,351 people) and Santa Catarina, with 0.66% (50,449 people).
In absolute numbers, the largest number of residents in CUs is in the state of São Paulo, with 2,483,199 (5.59% of its population), which accounts for 21.03% of the total population in CUs. It is followed by Maranhão, with 1,555,668 (22.96% of the population), and Bahia, with 1,354,144 (9.58%). Together, São Paulo, Maranhão, Bahia and Rio de Janeiro (1,118,507) account for more than half (55.14%) of the population living in CUs.
Nearly eight out of ten housing units in CUs are in urban situation
Of the total number of housing units in CUs, 78.71% are in urban situation and 21.29%, in rural situation. The Southeast and the Central-West stand out for the highest percentages of persons living in urban situation within CUs, 89.03% and 88.21%, respectively. The Federation Units with the highest proportion of persons living in urban situation in CUs are from those regions: Rio de Janeiro (95.87%); Espírito Santo (94.26%); Goiás (92.88%); and Federal District (91.17%).
In contrast, the North Region has the lowest percentage of the population living in urban situation within CUs (53.15%), followed by the Northeast (70.18%). In the North, the states with the highest weight of their resident population in CUs and rural situation stand out: Rondônia (90.23%); Amapá (84.60%); and Acre (80.65%).
Most people live in state CUs
Most people living in CUs live in areas under state administration, a total of 7,849,791 people, which corresponds to 66.47% of the total population living in CUs. The largest number of people in state CUs is in São Paulo, with 2,035,911 people, which corresponds to 81.99% of the population in these localities in the state. It is followed by Maranhão, with 1,486,636 people (95.56%) and Bahia, with 1,318,047 (97.33%). The states with the highest percentages of people's participation in state CUs are Rio Grande do Norte (99.98%), followed by Alagoas (98.71%) and Sergipe (98.67%). The lowest percentages, in turn, are found in Piauí (0.01%), Mato Grosso do Sul (0.92%) and in the Federal District (10.38%).
2,457,162 people live in federal CUs, which corresponds to 20.81% of the total resident population in CUs. In absolute terms, the Federal District houses the largest number of resident people, 908,788 (36.99%), followed by Ceará, with 299,052 people (12.17%), and Piauí, with 277,998 (11.31%). The highest percentages are found in Piauí, where 99.99% of the population living in CUs are under federal administration, followed by the Federal District, with 82.37% and Acre, with 71.38%.
Municipal CUs account for 10.94% (1,291,933) of the resident population. The municipality with most people living in CUs managed by the municipal administration is Rio de Janeiro (RJ), with 430,021 people, which corresponds to 33.29% of persons living in municipal CUs. It is followed by Sao Paulo (SP), with 136,270 (10.55%) and Manaus (AM), with 58,527 (8.53%).
From this publication on, the Geographic Reference Framework for the Production, Analysis and Dissemination of Statistics was updated with the inclusion of the geography Conservation Units, built from the data of the National Register of Conservation Units of the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change, with the collaboration of the Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation (ICMBio) and state and municipal managing offices.




















